By CIPESA Writer |
The police in Tanzania has detained Maxence Melo, a freedom of expression activist and co-founder of the popular online discussion platform, Jamii Forums. Although no charges have been brought against Melo, who was arrested at 1pm on Tuesday, December 13, his lawyer says the detention is an intimidation tactic on the backdrop of an ongoing case before the courts on the constitutionality of the Cybercrime Act of 2015.
The Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) strongly condemns this unjustifiable arrest, and urges Tanzanian authorities to immediately release Melo and henceforth cease any intimidation of Jamii Media (the company under which Jamii Forums is run), its staff, and other social media users. Melo’s arrest extends the steady and worrying deterioration in media freedom and internet freedom since President Pombe Magufuli took the reins of power at the end of last year. As one user on the platform noted, Jamii Forums provides Tanzanians with an alternative source of information in addition to “relying on traditional media outlets, which are increasingly becoming state-controlled.”
According to Melo’s lawyer, Benedict Alex Ishabakaki, the activist was arrested because of Jamii Media’s refusal to comply with police demands for disclosure of the identities of users who posted “sensitive information” on the platform. Last July, police officials issued a letter to Melo indicating intention to sue him for criminal liability for failure to comply with disclosure notices. In the letter, police put Melo on notice under Section 22 of the Cybercrimes Act 2015 for obstruction of investigations.
Section 22 of the Act states:
(1) A person who intentionally and unlawfully destroys, deletes, alters, conceals, modifies, renders computer data meaningless, ineffective or useless with intent to obstruct or delay investigation commits an offence and on conviction, is liable to a fine of not less than three million shillings or to imprisonment for a term not less than one year or both.
(2) A person who intentionally and unlawfully prevents the execution or fails to comply with an order issued under this Act, commits an offence and is liable, on conviction, to a fine of not less than three million shillings or to imprisonment for a term of not less than one year or to both.
See Cybercrimes Act 2015
A number of Tanzanian social media users have been charged under this law that took effect in September 2015. According to Ishabakaki, Jamii Media’s refusal to comply with the police disclosure notices was partly informed by a lack of regulations governing the Act. “At the time [the notices were issued], there were no mechanisms in place or procedures for disclosure of the requested information,” said Ishabakaki. Moreover, he added, “We refused to disclose the information because it is against the constitutional guarantees of individuals’ right to privacy under Article 18.”
In April 2016, after being issued with eight letters by Tanzanian police demanding the disclosure of the Internet Protocol (IP) addresses of users, Jamii Media went to court challenging the disclosure orders by the law enforcement agency. The users whose identities authorities sought were linked to bringing to light corruption scandals in the oil and banking sectors. According to the State of Internet Freedom in Africa 2016 report, the disclosure notices indicate a bias towards protecting notable figures implicated in scandals or against whom users have used profanities.
In its petition, Jamii Media challenged the arbitrary letters from the police and specifically the provisions of Section 32 and 38 of the Cybercrime Act that appear to infringe the right to be heard, the right to privacy and freedom of expression as provided for under the constitution. Initially, the government responded by raising six preliminary points of objection against the petition, which it termed frivolous and vexatious. The government stated that Jamii Media should explore other remedies rather than file a constitutional petition. During preliminary hearings, judges dismissed the objections and the case proceeded in court. A ruling on the case is due on February 20, 2017.
According to Ishabakaki, Melo’s detention tantamounts to police interference in the ongoing case, the issues of which are still before the constitutional court. “Police officers are misusing their power,” he said.
Prior to his arrest, Melo was summoned to appear in court, by way of telephone call. Upon arrival at the court, an officer told him to appear at a police station, where he was immediately detained.
“No charges have been filed. We were unable to apply for bail yesterday as the law requires detention for 24 hours before formal application of bail,” Ishabakaki told CIPESA on the morning of December 14. He added that police officials had indicated that Melo would appear in court this morning but as at 11am local time, this had not happened. “They are not prepared. It is just harassment. They want information from him,” said the lawyer.
Back in 2008, Melo, along with Jamii Forums co-founder Mike Mushi, were detained and interrogated by police for 24 hours in Dar es Salaam in what was believed to be a politically motivated attempt to shut down their site. Police confiscated computers used to host the website, causing it to go off air for five days while the equipment remained in police custody.
In September 2015, the Tanzania Human Rights Defenders Coalition (THRDC) filed a case challenging the constitutionality of some provisions of the Cybercrime Act, which it contends infringe constitutional provisions on freedom of expression, right to information, and privacy.
The Tanzanian government is accordingly urged to refrain from applying this law, or any other of the repressive laws that remain on its statute books, to gag legitimate expression by citizens be it in the online or offline domain.
#KeepitOn: Joint letter on the internet and the election in Gambia
President Yahya Jammeh
cc: Gambia Public Utilities Regulatory Authority (PURA)
Gambia Permanent Mission to the United Nations
African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights
30 November 2016
Your Excellency,
We are writing to urgently request that you ensure the stability and openness of the internet during the forthcoming elections in Gambia on December 1. Elections represent the most critical moment in a democracy, and the internet enables free expression and the fulfillment of all human rights.
However, we have received unconfirmed reports through a variety of sources that your government intends to shut down the internet. We implore you to keep the internet on.
Research shows that internet shutdowns and state violence go hand in hand. [1] Shutdowns disrupt the free flow of information and create a cover of darkness that allows state repression to occur without scrutiny. Worryingly, Gambia would be joining an alarming global trend of government-mandated shutdowns during elections, a practice that many African Union member governments have recently adopted, including: Burundi, Congo-Brazzaville, Egypt, Sudan, the Central African Republic, Niger, Democratic Republic of Congo. [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]
Internet shutdowns — with governments ordering the suspension or throttling of entire networks, often during elections or public protests — must never be allowed to become the new normal.
Justified for public safety purposes, shutdowns instead cut off access to vital information, e-financing, and emergency services, plunging whole societies into fear and destabilizing the internet’s power to support small business livelihoods and drive economic development. In addition, a study by the Brookings Institution indicates that shutdowns drained $2.4 billion from the global economy last year. [9]
International Law
A growing body of jurisprudence declares shutdowns to violate international law. The United Nations Human Rights Council has spoken out strongly against internet shutdowns. In its 32nd Session, in July 2016, the Council passed by consensus a resolution on freedom of expression and the internet with operative language on internet shutdowns. The resolution, A/HRC/RES/32/13, “condemns unequivocally measures to intentionally prevent or disrupt access to or dissemination of information online in violation of international human rights law and calls on all States to refrain from and cease such measures.” The Council intended this clear declaration to combat the blocking and throttling of networks, applications, and services that facilitate the freedoms of expression, opinion, and access to information online. In addition, the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights stated in its November 2016 Resolution on the Right to Freedom of Information and Expression on the Internet in Africa that it was “Concerned by the emerging practice of State Parties of interrupting or limiting access to telecommunication services such as the Internet, social media and messaging services, increasingly during elections.” [10]
In 2015, various experts from the United Nations (UN) Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), Organization of American States (OAS), and the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights (ACHPR), issued an historic statement declaring that internet “kill switches” can never be justified under international human rights law, even in times of conflict. [11] General Comment 34 of the UN Human Rights Committee, the official interpreter of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, emphasizes that restrictions on speech online must be strictly necessary and proportionate to achieve a legitimate purpose. Shutdowns disproportionately impact all users, and unnecessarily restrict access to information and emergency services communications during crucial moments.
The internet has enabled significant advances in health, education, and creativity, and it is now essential to fully realize human rights including participation in elections and access to information.
We humbly request that you use the vital positions of your good offices to:
- Ensure that the internet, including social media, remains on in Gambia throughout the election and beyond
- Publicly declare your commitment to keep the internet on, including social media
- Encourage telecommunications and internet services providers to respect human rights, including through public disclosures and transparency reports.
We are happy to assist you in any of these matters.
Sincerely,
Access Now
Association for Progressive Communications (APC)
CIPESA
Heliopolis Institute
Human Rights Foundation
iFreedom Uganda
Internet Sans Frontières
Media Foundation for West Africa
Paradigm Initiative Nigeria
Social Media Exchange (SMEX)
Strathmore University Centre for IP and It Law (CIPIT)
Unwanted Witness Uganda
[1] Sarah Myers West, ‘Research Shows Internet Shutdowns and State Violence Go Hand in Hand in Syria’ (Electronic Frontier Foundation, 1 July 2015)
<https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2015/06/research-shows-internet-shutdowns-and-state-violence-go-hand-hand-syria> accessed 18 February 2016.
[2] ‘Access urges UN and African Union experts to take action on Burundi internet shutdown’ (Access Now 29 April 2015) <https://www.accessnow.org/access-urges-un-and-african-union-experts-to-take-action-on-burundi-interne/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[3] Deji Olukotun, ‘Government may have ordered internet shutdown in Congo-Brazzaville’ (Access Now 20 October 2015) <https://www.accessnow.org/government-may-have-ordered-internet-shutdown-in-congo-brazzaville/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[4] Deji Olukotun and Peter Micek, ‘Five years later: the internet shutdown that rocked Egypt’ (Access Now 21 January 2016) <https://www.accessnow.org/five-years-later-the-internet-shutdown-that-rocked-egypt/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[5] Peter Micek, ‘Update: Mass internet shutdown in Sudan follows days of protest’ (Access Now, 15 October 2013) <https://www.accessnow.org/mass-internet-shutdown-in-sudan-follows-days-of-protest/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[6] Peter Micek, ‘Access submits evidence to International Criminal Court on net shutdown in Central African Republic’(Access Now 17 February 2015) <https://www.accessnow.org/evidence-international-criminal-court-net-shutdown-in-central-african-repub/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[7] ‘Niger resorts to blocking in wake of violent protests against Charlie Hebdo cartoons.’ (Access Now Facebook page 26 January 2015) <https://www.facebook.com/accessnow/posts/10153030213288480> accessed 18 February 2016.
[8] Peter Micek, (Access Now 23 January 2015) ‘Violating International Law, DRC Orders Telcos to Cease Communications Services’ <https://www.accessnow.org/violating-international-law-drc-orders-telcos-vodafone-millicon-airtel/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[9] Darrell West, (Brookings Institution, October 2016) “Internet shutdowns cost countries $2.4 billion last year” https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/intenet-shutdowns-v-3.pdf
[10] African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights, (November 2016) ‘362: Resolution on the Right to Freedom of Information and Expression on the Internet in Africa – ACHPR/Res. 362(LIX) 2016’ http://www.achpr.org/sessions/59th/resolutions/362/
[11] Peter Micek, (Access Now 4 May 2015) ‘Internet kill switches are a violation of human rights law, declare major UN and rights experts’ <https://www.accessnow.org/blog/2015/05/04/internet-kill-switches-are-a-violation-of-human-rights-law-declare-major-un> accessed 18 February 2016.
This join letter first appeared on the Access Now website
Fostering the Right to Information Among Women’s Rights Organisations in Uganda
By Juliet Nanfuka |
Goal 5 of the Sustainable Development Goals is to ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision making in political, economic and public life. Access to information is necessary in advancing gender equality and women’s participation in governance processes.
Accordingly, the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) is undertaking a series of engagements to create awareness of the right to information law in Uganda and the avenues through which women’s rights organisations can exercise this right to empower women in the country.
At a training on November 11, 2016, 12 representatives from women’s organisations discussed the relationship between women’s rights and the right to information with a focus on how to utilise Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to bridge the two rights. Specifically, SDG 5b calls for enhancing the use of technology, in particular ICT, to promote the empowerment of women.
Ashnah Kalemera, CIPESA’s Programmes Officer, noted that, “For the realisation of women’s rights and indeed many other rights in Uganda, the role that access to information plays should be better understood and should not be seen as exclusive of other rights such as non-discrimination, privacy and right to health.” She added that, “it is every citizen’s right to have access to information held by the state. However, this is challenged by the lack of awareness to demand information which would enable a more transparent and accountable state and ultimately citizens who can make informed decision on issues that affect them.”
“Every citizen has a right of access to information in the possession of the State or any other organ or agency of the State except where the release of the information is likely to prejudice the security or sovereignty of the State or interfere with the right to the privacy of any other person.” Article 41 of the Uganda Constitution
Training participants noted that the unavailability of information hampers civil society organisations’ engagement on pertinent social issues, as they often cannot develop in-depth reports or make interventions to empower women on the basis of strong evidence.
The use of ICT as an enabler of access to information has long been recognised by Uganda citizens and officials alike, however, platforms such as the online information request portal Ask Your Gov are providing an avenue for ordinary citizens and organisations with limited access or technical skills to request information . The portal allows for information requests submitted and responses given to be seen by anyone who accesses the website.
At the training, participants assessed information requests on the portal and their relevance to women’s rights and submitted information requests of their own. Loyce Mugisa from the National Association of Women Organisations in Uganda (NAWOU) said a highlight from the training was discovering “the amount of information available that we did not know about.” She added that she placed an information request on the portal and within a few minutes received a response from the land ministry. According to the law, public officials have 21 days within which to respond to an information request, which has often been cited “too long” to wait. “Encouraged” by the prompt response to her query, Mugisa has since sent a follow up question. See the interaction here.
Long held skepticism about the voluntary release of public information by the state has contributed to the poor use of the law. This is also due to conflicts with existing laws such as the Official Secrets Act.
Nonetheless, participants at the training reported an enthusiasm about the applicability of the law in their organisations to serve women’s interests.
*Organisations represented at the training included Alliance for Women in Development, Eastern African Sub-Regional Support Initiative for the Advancement of Women (EASSI), Isis-Women’s International Cross-Cultural Exchange (Isis-WICCE), National Union of Women with Disabilities (NUWD), National Association of Women Organisations in Uganda, Uganda Association of Women Lawyers (FIDA), Uganda Media Women’s Association (UMWA), Women’s Democracy Network (WDN Uganda), Women And Girl Child Development Association (WEGCDA), Women of Uganda Network (WOUGNET), and Young Women’s Christian Association (YWCA-Uganda),
CIPESA’s engagements on women’s rights and access to information are supported by the Association for Progressive Communications (APC).
Using SMS to Promote the Right to Health in Tanzania
Tweet
By Ashnah Kalemera |
In pursuit of strategic mechanisms to promote and protect human rights in Tanzania, the Commission for Human Rights and Good Governance (CHRAGG) has this year embraced the use of digital technologies to advance the right to health among vulnerable communities and human rights practitioners in five regions in Tanzania.

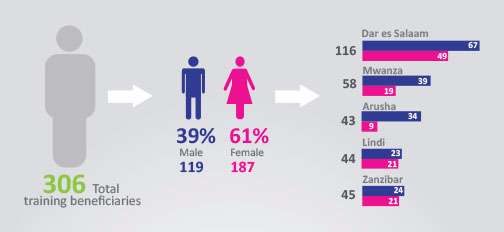
In August 2016, CHRAGG embarked on a campaign that leverages its SMS for Human Rights reporting system to improve rights awareness and protection for some hitherto marginalised groups. Under the drive, up to 100 commission staff at the head office in Dar es Salaam and three regional offices (Mwanza, Lindi and Zanzibar) have been trained to improve their understating of the right to health and to enable them to appropriately handle related violation reports received through the digital platform.
The CHRAGG training also benefited 190 individuals including sex workers, the elderly, women, health practitioners and local leaders who were trained on the principles of the right to health and how to monitor and report rights violations. Most of the training beneficiaries (61%) were female.
Breakdown of training beneficiaries
By Gender

By category

Vulnerable and marginalised communities such as indigenous people, women, and sexual minorities are often less likely to enjoy the right to health. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), achieving all citizens’ right to health is closely related to other human rights including non-discrimination, access to information and participation.
The right to health includes both freedoms and entitlements.
Freedoms include the right to control one’s health and body (e.g. sexual and reproductive rights) and to be free from interference (e.g. free from torture and from non-consensual medical treatment and experimentation).
Entitlements include the right to a system of health protection that gives everyone an equal opportunity to enjoy the highest attainable level of health.
See WHO Health and Human Rights Factsheet
As a result of the training, CHRAGG staff have better understanding of minority rights and have incorporated this knowledge into their daily work. As stated by one staff member, the training enabled them to make the link between the right to health, free expression and equality. “I never thought [other rights] are covered in right to health,” he said. Another noted, “I did not know [that] the commission could be involved in this,” referring to protection of the right to health.
However, training participants highlighted concerns in using the system such as slow resolution of reports. Going forward, commission staff are expected to specifically categorise health rights violation reports received from minority and vulnerable groups as part of case handling procedures and work towards their speedy resolution.
In December 2012, CHRAGG launched the SMS for Human Rights System to make it easier for citizens to report human rights violations. Since then, the commission has conducted campaigns throughout Tanzania to raise awareness about the system. This has greatly boosted the number of reports received through SMS.

The commission is developing and testing a minority groups’ database within the existing complaints handling system. Once implemented, the database will enable toll-free human rights violations reporting for minorities, efficient and confidential case management and follow-up, as well as disaggregation of statistics on minority rights abuses
Established in 2001 in fulfillment of Tanzania’s national constitution, CHRAGG plays the dual role of an ombudsman and a human rights commission for the protection and promotion of human rights and good governance.
CHRAGG is a member of the ICT4Democracy in East Africa Network whose work is supported by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida) and the Swedish Programme for ICT in Developing Regions (Spider). The network is coordinated by the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA).
Amplifying Community Rights Through Social Media in Kenya
Tweet
By Ashnah Kalemera |
Human rights violations incidents are on the rise in Kenya with extrajudicial killings and police brutality among the cases reported recently. Social media has enabled quick reporting of such cases while also creating increased awareness of the reported incidents. Through a mix of Twitter, radio and physical engagements, the Kenya Human Rights Commission (KHRC) is improving its effectiveness in promoting human rights and documenting violations in the lead up to the 2017 national elections.
The commission is seeing success in mobilising citizens for protests and marches, as well as getting stakeholders to participate in debates related to human rights. Through quarterly Twitter chats, the KHRC is popularising various human rights issues and bringing to the fore struggles faced by communities that have little online presence and who have limited avenues for participating in community affairs.
A Twitter chat hosted in September 2016 to promote dialogue on governance and anti-corruption drew panelists from the Institute of Economic Affairs (IEA-Kenya), Transparency International Kenya, International Commission of Jurists (ICJ)-Kenya, Society for International Development and Kenya Association of Manufacture (KAM).
Another chat on insecurity (under the hashtag #InSecurityKE) hosted in July 2016 explored the causes of social insecurity, challenges faced in addressing it and proposals for over coming those challenges. Panelists included the Kenya National Commission
coming those challenges. Panelists included the Kenya National Commission
on Human Rights, Amnesty International Kenya, Independent Medico-Legal Unit (IMLU) and ICJ-Kenya.
In another drive, the KHRC on October 10-13, 2016 mobilised 300 members of the Makonde community who live along the south eastern coast of Kenya for a walk dubbed “Trek against Statelessness”, from Kwale county to the capital Nairobi. The walk was in protest against the exclusion of the community from attaining formal national recognition and identity documentation. Several members of the Makonde community have lived in Kenya for about half a century after many of them immigrated from Mozambique.
Upon arrival at the State House, President Uhuru Kenya gave audience to the community and promised that all of the members would be registered as citizens. The registration process kicked off on October 24 and ended on November 10, 2016.
In the weeks leading up to the walk, among the channels utilised by the commission to mobilise participants were online platforms, with the hashtag #MKenyaNiWho (“Who is a Kenyan”) used to raise awareness of the Makonde community’s plight. Furthermore, a radio talk show was hosted on Citizen Radio for the Kwale Human Rights Network to discuss issues of registration of the Makonde community as Kenya Citizens.
Earlier in July, citizenship and statelessness, identity and belonging were also discussed at the Samosa Festival in Kenya. Among the key areas of discussions were the difficulties faced by Kenyans of Somali descent when applying for national identity cards and birth certificates in the northern part of the country. The discussion attracted members of parliament and members of communities that are struggling with the issue of citizenship.
Meanwhile, to support its efforts at grassroots level, KHRC has built the capacity of 14 Human Rights Networks (Hurinets) in four regions – Mombasa, Nairobi, Kisumu and Nyeri – to engage on issues of electoral governance and devolution including through social media. The beneficiary Hurinets included Kwale, Mombasa, Kinangop, Taita Taveta, Kakamega, Siaya, Migori, Nairobi, Makueni, Wajir, Nakuru, Nyeri, Kiambu and Isiolo. A total of 103 members of the networks (57% male and 43% female) have benefitted from the training.
The increased capacity of the Hurinets in Kenya to promote discussions on human rights issues in remote and rural areas where the Hurinets are based is expected to contribute to more issues being brought to the attention of local and national government primarily through social media. In 2015, the Midrift Hurinet in Nakuru County started #UwajibikajiMashinani “AccountabilityInRuRalAreas” hashtag campaign to get more citizens to deliberate on issues of accountability in the county. The Kwale Hurinet started #OkoaKwaleInitiative and “SaveKwaleInitiative” hashtag campaigns that asked Kwale county government leaders not to allow petty, personal differences to influence community decisions.
KHRC is a member of the ICT4Democracy in East Africa Network whose work is supported by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida) and the Swedish Programme for ICT in Developing Regions (Spider). The network is coordinated by the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA).
See also ICT4Democracy in East Africa Annual Report 2015 and using technology to advance human rights in Kenya.