Call for Applications |
The Annenberg School for Communication’s Internet Policy Observatory, the Collaboration on
International ICT Policy in East and Southern Africa (CIPESA), Research ICT Africa, Kenya ICT Action Network (KICTANet), Unwanted Witness, Paradigm Initiative, and
Young ICT Advocates seek applications from young scholars, activists, lawyers, and technologists working across Africa for an intensive practicum on using research for digital rights advocacy.
The workshop seeks to provide a venue for stakeholders in the region to build collaborative possibilities across sectors, expand research capacity within practitioner and digital rights advocacy communities, and to provide the skills and know-how to more strategically use research and data to advance advocacy efforts. Sessions will cover both qualitative and quantitative methods and will provide the space for hands-on activities and the development of individual and group research interests. In this way, the workshop seeks to provide opportunities to connect scholarly expertise with policymakers and advocates and improve working synergies between emerging African networks of civil society organizations, academic centers and think-tanks.
Sessions will include workshops on stakeholder analysis, conducting interviews, researching laws and regulations, social network analysis, network measurement, survey methods, data visualization, and strategic communication for policy impact.
We encourage individuals from Africa in the academic (early career), NGO, technology, and public policy sectors to apply. Prospective applicants should have a particular area of interest related to internet governance and policymaking, censorship, surveillance, internet access, political engagement online, protection of human rights online, and/or corporate governance in the ICT sector. Applicants will be asked to bring a specific research question to the program to be developed and operationalized through trainings, group projects, and one-on-one mentorship with top researchers and experts from around the world. Several partial and full scholarships will be made for the most competitive applicants to participate.
The course will be conducted in English and applicants should have high proficiency in English in order to interact with experts, lecturers and other participants who will come from diverse backgrounds. Please also note that we require all participants to have a laptop to use for the duration of the program.
Application Deadline: November 10, 2017
Workshop Dates: Feb 26 – Mar 3, 2018 | Location: Kampala, Uganda
To apply for the program, please fill this form.
For questions, please email Laura at [email protected].
About FIFAfrica
The Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) and the Association for Progressive Communication (APC) are proud to co-host the 2017 edition of the Forum on Internet Freedom in Africa (FIFAfrica).
This year’s Forum will be held in Johannesburg, South Africa, thus expanding the physical footprint of the Forum which has since inception in 2014 been held in Kampala, Uganda. The landmark event convenes various stakeholders from the internet governance and online rights arenas in Africa and beyond to deliberate on gaps, concerns and opportunities for advancing privacy, access to information, free expression, non-discrimination and the free flow of information online.
The Forum brings together human rights defenders, journalists, government officials, private sector players, global information intermediaries, bloggers, developers, the arts community, law enforcers and regulators – all of whom have a role to play in advancing internet freedom in Africa.
Highlights at FIFAfrica include the launch of the annual State of Internet Freedom in Africa research report, the commemoration of the International Day for Universal Access to Information (IDUAI) that falls on September 28, digital security clinics and this year, an exhibition showcasing the work and products of various players in the internet freedom arena in Africa.
Read more about FIFAfrica here
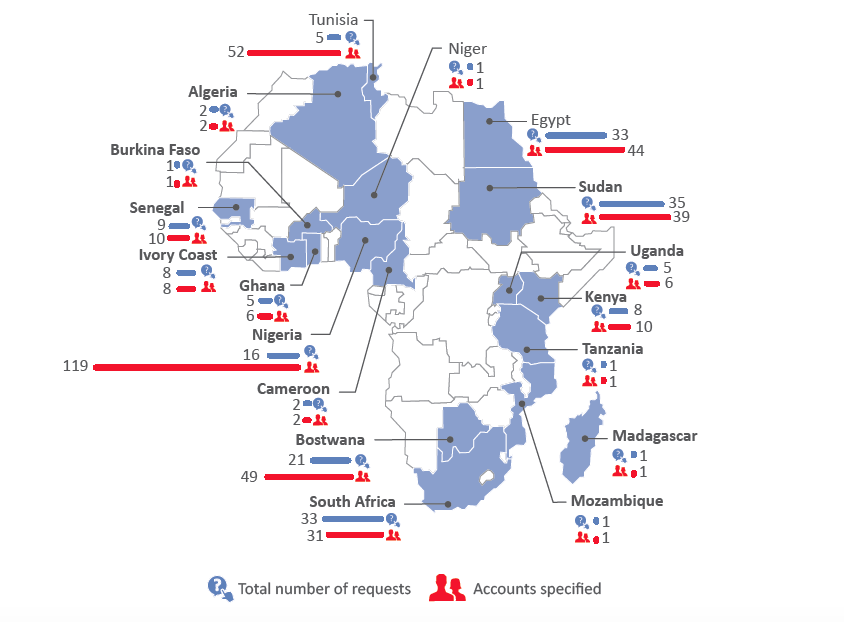
The Growing Trend of African Governments’ Requests for User Information and Content Removal From Internet and Telecom Companies
Policy Brief |
The relationship between communications service providers, users and governments with regards to data protection, requests of user information and content take downs is increasingly taking centre stage in discussions around free, open and secure use of digital technologies.
In February 2017, Millicom issued its second Law Enforcement Disclosure Report. Millicom’s report is one of many by private companies aimed at promoting transparency and accountability, through periodically publishing reports detailing information on government requests for user data, content removals, and compliance with those requests.
Google is credited with being the first internet company to publish a transparency report back in 2009, followed by Twitter in 2012. Facebook and Yahoo have published reports since 2013. Vodafone and Orange were among the first telecommunications companies to publish transparency reports, both in 2014.
These reports have become vital to understanding censorship, surveillance and more importantly the commitment of service providers to protecting the privacy of their users and promoting freedom of expression online. Based on the reports alone, it remains unclear what the true extent of governments’ surveillance of citizens’ communications and censorship of content across the world is. Nonetheless, the reports indicate a growing trend among countries, including African governments, of requests for subscribers’ data and content removal.
On the social media front, from five African countries being listed by Facebook among those that requested users’ details in the first half of 2013, the number on the continent has grown to 18 as at the end of 2016. Meanwhile, requests to remove content from Google have also grown from only Libya in 2010 and 2011, to four African countries in 2016 alone. Twitter, which only received one user information request from South Sudan in 2012, has since gone on to receive requests from an additional four countries on the continent. The countries which have consistently made requests for user information to Google, Facebook and Twitter include South Africa, Nigeria, Sudan, Kenya and Egypt.
In telecommunications, figures are scanty as only four companies operating in Africa issue transparency reports – one of which, MTN, does not disclose any statistics while Vodafone’s extent of disclosure is limited due to legal provisions in some of its countries of operation that prohibit publishing of such information. Even then, user data requests from five African governments to Millicom have increased from 5,000 in 2015 to nearly 7,000 in 2016. Requests to Orange from the 20 African countries where it had operations as at the end of 2016 have tripled in the past three years – from 22,930 in 2014 to 67,718 in 2016.
In this brief, we provide a summary of the user data and content removal requests which governments in Africa have made to select internet and telecommunications companies in recent years.
Promoting Youth Participation in Governance Through ICT in Kenya
By Tracy Kadesa |
Youths have emerged at the forefront of online activism and citizen journalism in Kenya. During a December 2016 to March 2017 strike by doctors, young doctors shared their grievances online, ranging from lack of resources in government hospitals to inadequate staffing and poor compensation. One of the stories was that of Dr. Ouma Oluga, the secretary general of the Kenya Medical Practitioners, Pharmacists and Dentists Union, who shared how he had to perform a caesarean section using a torch on his mobile phone due to a power outage. He was only 27 at the time.
Ahead of Kenya’s elections scheduled for August 2017, there have been increased calls for young Kenyans to participate in related processes and vote as a means of positively influencing concerns such as the high rates of unemployment. According to a 2016 World Bank report, Kenya has among the highest youth unemployment rates in Africa.
Against this background, on May 9-10, 2017, the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) convened 30 youth and civil society activists to explore rights and responsibilities, as well as effective and secure ways to engage in the country’s governance processes including through ICT.
The workshop raised awareness about various ICT-based initiatives that have given Kenyan youths an opportunity to regularly discuss issues and analyse the manifestos of candidates running for elective posts. For instance, SiasaPlace runs weekly Twitter chats using #SiasaWednesday with the aim of amplifying women and youth voices. Siasa Place is a hub and co-working space that is passionate about engaging youth and women on civic agency.
Tribeless Youth is another vibrant movement that uses Twitter to engage youth in governance. Ongoing discussions facilitated by #TribelessYouth include #MeetTheNewCandidates where first-time political candidates, mostly youthful ones, are given an opportunity to present what they plan to deliver if elected come August.
Other youth-led initiatives that participated in the workshop included Fatuma’s Voice, a youth empowerment organisation, and Centre for Public Engagement & Social Economic Affairs Kenya (CPESEAK), which works on promoting youth participation in social accountability. Irungu Houghton of Society for International Development; Kenya Dialogues Project (KDP) participated as guest speaker and highlighted KDP’s commitment to advancing youth leadership in Kenya.
The workshop also explored government efforts to motivate the youth to participate in the August 2017 general elections through an initiative dubbed Y-VOTE (Youth Vote). The initiative spearheaded by the Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC) in partnership with the International Foundation for Electoral systems (IFES) leverages social media and on-ground activations to mobilise 18-29 year olds to vote come August 8. The campaign was launched on June 20, 2017 and run to late July.
Participants in the workshop explored ways of leveraging the various civic agency and elections-related initiatives to exercise their rights but also champion a peaceful electioneering period through online activism. Furthermore, discussions entailed digital safety tools and practices to facilitate secure communications.
The participants agreed that they were “no longer leaders of tomorrow but of today” and it was therefore their duty to zealously participate in governance processes towards improved livelihoods. See more insights in video below.
The youth in governance in Kenya workshop was organised in the context of the ICT4Democracy in East Africa initiative which is aimed at leveraging ICT to promote civic participation, democratic governance and respect for human rights.
Young Social Media Enthusiasts in Kenya Trained on Internet Law and Digital Security
By Shitemi Khamadi |
In 2015, Allan Wadi, became the first Kenyan to be convicted of hate speech online. At a May 2017 training on internet and the law, he expressed gratitude for the opportunity to acquire skills and knowledge to avoid future arrest and prosecution. While he is currently facing an incitement to violence charge over a comment he made on Facebook in February 2016, he said he is now more aware of the extent of his rights and limitations with respect to the rights of others.
Wadi is however convinced that the various charges brought against him were unfair as many others who have made similar and according to him, graver comments online have gone unpunished. “I feel it was to set me as an example”, he remarked at the end of the training in Kisumu where 43 other youth including technology enthusiasts, communications students and bloggers were trained in the legal frameworks governing use of the internet in Kenya.
See: Allan Wadi Feels Arrests and Charges are Unfair
The objective of the training hosted by the Bloggers Association of Kenya (BAKE) in partnership with the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) was to build participants’ understanding of rights and offenses related to the internet within the Kenyan legal context. The training was organized in light of shrinking rights of Kenya’s digital citizens in the face of new restrictive laws and increased arraignment of individuals for expressing online opinions which authorities deem in breach of the law, especially given the upcoming electioneering period.

Prior to the Kisumu training, a similar training was held in Nairobi where a Senior Prosecutor in the office of the Director of Public Prosecutions (DPP), Duncan Ondimu, was unequivocal that his office would be more vigilant on hate speech cases online, arrest any perpetrator and charge them in court. “We will not spare anyone,” said Ondimu who also serves as the Senior Prosecution Counsel. He added that the DDP had set up a 24 hour toll free line to for citizens to report hate speech offenses from social media posts that the office would follow up with investigations. Kenyans can also report offences to the DPP on Facebook and Twitter.
Furthermore, Ondimu stated that while the country had made gains in removing clauses in various laws that limited freedom of expression, provisions relating to defamation still exist. In 2016, Section 29 of the Kenya Information and Communications Act, Section 194 of the Penal Code and Section 132 of the Penal code were declared unconstitutional.
Nonetheless, a key concern among participants in the two trainings was user safety online. In particular, combating harassment, stalking and cyber bullying especially against women. Digital security trainer Ephraim Muchemi took participants through communications and device protection practices including strong passwords, anti viruses, encryption (email and hard disk) and privacy settings on social media accounts.
Mr. Wadi challenged the bloggers and social media users to become the main source of information even for the mainstream media in documenting events during the election. “You should also act like observers and update electorates of the voting and tallying processes from various tallying centres”, he asserted.
He also urged BAKE and similar actors to continue with capacity building efforts aimed at empowering bloggers and social media activists, as well as supporting them during litigation over offences.
The trainings were organized in the context of the ICT4Democracy in East Africa initiative as part of efforts to promote ICT enabled participation in governance pre and post elections in Kenya.