Par Abdou Aziz Cissé, Laïty Ndiaye et rédacteur du CIPESA |
Le report des élections présidentielles au Sénégal en février 2024 a exacerbé les tensions politiques dans le pays d’Afrique de l’Ouest. En réponse, le Ministère de la Communication, des Télécommunications et de l’Économie Numérique a suspendu l’accès à Internet mobile, d’abord le 5 février alors que le parlement débattait de la prolongation du mandat du Président Macky Sall, puis à nouveau le 13 février au milieu de manifestations de la société civile. Le ministère a affirmé que les plateformes de médias sociaux alimentaient la diffusion de “plusieurs messages haineux subversifs” incitant à la violence.
Les restrictions de février 2024 sur l’accès à Internet mobile constituaient la troisième instance de perturbations du réseau dans le pays, qui avait précédemment maintenu l’accès à Internet disponible lors de moments cruciaux, notamment les élections. L’année dernière, le Sénégal a restreint l’accès à Internet et interdit TikTok, au milieu de manifestations de l’opposition.
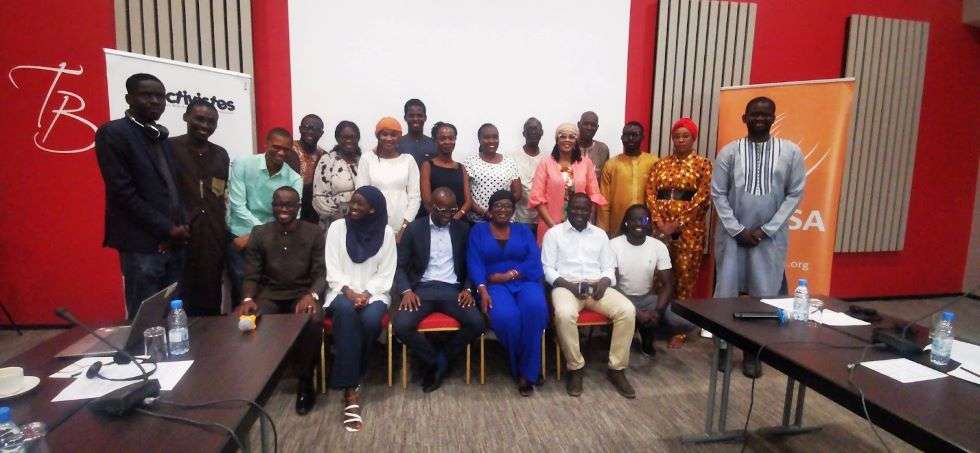
C’est dans ce contexte que la Collaboration sur les Politiques Internationales des TIC pour l’Afrique de l’Est et Australe (CIPESA), en partenariat avec AfricTivistes, a organisé un atelier sur la responsabilité des plateformes et la modération du contenu le 8 février 2024. L’atelier, qui s’est tenu dans la capitale Dakar, a examiné l’efficacité et l’impact de la modération du contenu et a discuté des opportunités de collaboration entre les parties prenantes et des approches communes pour promouvoir la liberté d’Internet au Sénégal.
En septembre 2023, il y avait plus de 18 millions d’abonnés à Internet au Sénégal. Les participants à l’atelier ont reconnu que la croissance du nombre d’utilisateurs alimentait la désinformation en ligne et les discours de haine, qui menacent la cohésion sociale. Cependant, ils ont également exprimé des préoccupations concernant les réponses disproportionnées, notamment les perturbations du réseau instituées par le gouvernement, qui portent atteinte à la liberté d’expression, à l’accès à l’information et à la participation citoyenne.

Selon Ababacar Diop, Commissaire à la Commission de Protection des Données Personnelles (CDP), les efforts visant à freiner la diffusion de contenus nuisibles et illégaux en ligne ont conduit la Commission à collaborer avec des plateformes de médias sociaux populaires pour explorer des mécanismes permettant de réguler efficacement le contenu. Il a ajouté cependant que, comme les plateformes ne sont pas domiciliées au Sénégal, l’effet du partenariat a été limité. En plus d’être l’autorité chargée de la protection des données personnelles, le mandat de la CDP comprend également la garantie que la technologie ne constitue pas une menace pour les droits et la vie des citoyens.
Les engagements de la CDP avec les plateformes complétaient les signalements d’utilisateurs concernant des contenus nuisibles et illégaux et le programme de partenariat de confiance. Cependant, les participants ont noté que les signalements d’utilisateurs et les programmes de partenariat de confiance étaient fortement subjectifs, les utilisateurs et les partenaires signalant parfois des contenus comme inappropriés ou dangereux “uniquement sur la base de leurs opinions”. “Les politiques de modération des plateformes et des gouvernements doivent tenir compte des contextes et opinions différents”, a déclaré Serge Koué, blogueur et expert en technologie de l’information. De plus, les mesures de modération du contenu basées sur des algorithmes sont également sujettes au même défi, car elles ne comprennent pas le contexte local et les langues, selon Pape Ismaïla Dieng, Responsable de la Communication et du Plaidoyer chez AfricTivistes.
Les complexités liées à la modération du contenu ont été mises en lumière avec des études de cas du Nigeria et de l’Ouganda. En 2021, l’ancien Président nigérian Muhammadu Buhari a annoncé une interdiction nationale de Twitter suite à la suppression d’un tweet de son compte sur la guerre civile du Biafra. Twitter a affirmé que le tweet violait la politique de la plateforme sur “le comportement abusif”. Twitter a été bloqué dans le pays à la suite de cet affrontement. En octobre 2021, le gouvernement a émis plusieurs conditions pour lever l’interdiction. Il exigeait que Twitter ouvre un bureau local, paie des impôts localement et coopère avec le gouvernement nigérian pour réguler les tweets nuisibles. La plateforme est restée interdite dans le pays jusqu’en janvier 2022.
En Ouganda, pendant la période électorale de 2021, Facebook et Twitter ont suspendu les comptes de divers individus pro-gouvernementaux pour ce que Facebook a décrit comme “Comportement Inauthentique Coordonné (CIC)” afin de servir les intérêts narratifs en ligne du parti au pouvoir. Les actions des plateformes ont suscité la colère du Président Yoweri Museveni qui a répondu en déclarant lors d’une allocution nationale que : “Si vous voulez prendre parti contre le (parti au pouvoir), alors ce groupe n’opérera pas en Ouganda”, ajoutant que : “Nous ne pouvons pas tolérer cette arrogance de quiconque venant décider pour nous qui est bon et qui est mauvais.” Un jour plus tard, le 11 janvier 2021, l’accès aux médias sociaux a été bloqué et deux jours plus tard, Internet dans son ensemble a été bloqué alors que les citoyens se préparaient à aller voter. Facebook reste bloqué à ce jour.
Les expériences du Nigeria et de l’Ouganda ont mis en lumière non seulement le rôle des personnalités publiques en tant qu’auteurs de contenus nuisibles, mais aussi l’impact du pouvoir non contrôlé des gouvernements pour censurer et restreindre l’accès aux plateformes en réponse directe à la modération du contenu basée sur les Normes Communautaires des plateformes.
Pendant l’atelier, Olivia Tchamba, Responsable des Politiques Publiques de Meta pour l’Afrique francophone, a déclaré que la plateforme s’engageait à trouver un équilibre entre donner la parole aux utilisateurs et garantir la prédominance de l’information fiable. Elle a ajouté que la réglementation associée à un comportement utilisateur responsable devrait être la norme.
La Directrice de Programme de CIPESA, Ashnah Kalemera, a également souligné que la modération du contenu nécessite une approche multi-parties prenantes et multifacette impliquant non seulement les plateformes et les régulateurs, mais aussi les utilisateurs.
L’atelier, auquel ont participé 25 personnes, dont des journalistes, des influenceurs des médias sociaux, des défenseurs des droits de l’homme et du personnel d’organisations de la société civile, a appelé les plateformes à garantir que leurs conditions d’utilisation soient disponibles dans plusieurs langues, à accroître la transparence de leurs processus de modération du contenu, et à promouvoir la sensibilisation et la compréhension des utilisateurs africains sur les mécanismes de recours.
Ils ont également souligné que la consolidation des efforts, tels que ceux de la société civile, du CDP et du Conseil de Surveillance de Meta, conformément aux lois nationales et aux normes internationales en matière de droits de l’homme, contribuerait à créer un écosystème des médias sociaux qui défend la liberté d’expression et la vie privée, entre autres droits. Alors que la Cour Constitutionnelle sénégalaise s’est prononcée contre le report des élections, une nouvelle date pour les élections reste à déterminer. Le dialogue lors de l’atelier de CIPESA et d’AfricTivistes est crucial alors que les tensions continuent de bouillonner en ligne et hors ligne, et donne le ton pour des engagements similaires dans d’autres pays africains devant se rendre aux urnes en 2024 et pour la promotion de la responsabilité accrue des technologies.