Policy Brief |
The relationship between communications service providers, users and governments with regards to data protection, requests of user information and content take downs is increasingly taking centre stage in discussions around free, open and secure use of digital technologies.
In February 2017, Millicom issued its second Law Enforcement Disclosure Report. Millicom’s report is one of many by private companies aimed at promoting transparency and accountability, through periodically publishing reports detailing information on government requests for user data, content removals, and compliance with those requests.
Google is credited with being the first internet company to publish a transparency report back in 2009, followed by Twitter in 2012. Facebook and Yahoo have published reports since 2013. Vodafone and Orange were among the first telecommunications companies to publish transparency reports, both in 2014.
These reports have become vital to understanding censorship, surveillance and more importantly the commitment of service providers to protecting the privacy of their users and promoting freedom of expression online. Based on the reports alone, it remains unclear what the true extent of governments’ surveillance of citizens’ communications and censorship of content across the world is. Nonetheless, the reports indicate a growing trend among countries, including African governments, of requests for subscribers’ data and content removal.
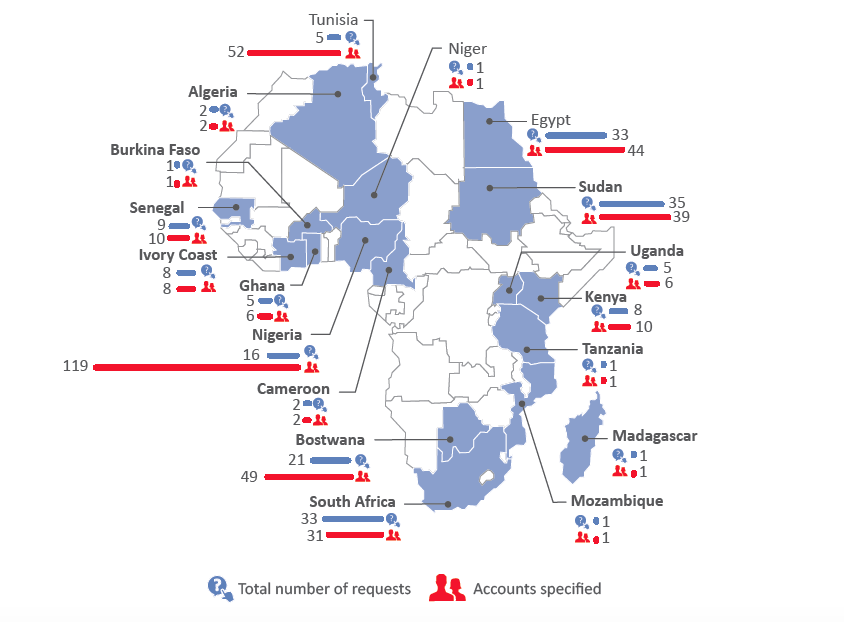
On the social media front, from five African countries being listed by Facebook among those that requested users’ details in the first half of 2013, the number on the continent has grown to 18 as at the end of 2016. Meanwhile, requests to remove content from Google have also grown from only Libya in 2010 and 2011, to four African countries in 2016 alone. Twitter, which only received one user information request from South Sudan in 2012, has since gone on to receive requests from an additional four countries on the continent. The countries which have consistently made requests for user information to Google, Facebook and Twitter include South Africa, Nigeria, Sudan, Kenya and Egypt.
In telecommunications, figures are scanty as only four companies operating in Africa issue transparency reports – one of which, MTN, does not disclose any statistics while Vodafone’s extent of disclosure is limited due to legal provisions in some of its countries of operation that prohibit publishing of such information. Even then, user data requests from five African governments to Millicom have increased from 5,000 in 2015 to nearly 7,000 in 2016. Requests to Orange from the 20 African countries where it had operations as at the end of 2016 have tripled in the past three years – from 22,930 in 2014 to 67,718 in 2016.
In this brief, we provide a summary of the user data and content removal requests which governments in Africa have made to select internet and telecommunications companies in recent years.
Join us at the Forum on Internet Freedom in Africa 2017 (FIFAfrica17): Register Today!
Register and join those who already have set their sights on joining us at #FIFAfrica17 as we continue to advocate for an internet that is free, secure and open. We have received many session proposals and suggestions but are still open to receiving a few more. As you register, you are still welcome to add your suggestion – we’ll try our best to find a way of addressing the topics you raise. Successful session proposals will be listed on the Forum webpage on August 10, 2017.
Travel Support
Last year we received over 400 applications for travel support of which we were able to support less than one-fifth of the applicants. Our vision is to have a Forum with representation from as many countries in Africa as possible. As part of the registration process, we make room for interested participants to submit an application for travel support.
Exhibit at #FIFAfrica17
Participation in the Forum takes various forms. Some want to talk, others want to listen and some want to show what they do. We are expanding exhibition space at the Forum and are thus inviting proposals from individuals,organisations and companies who wish to showcase their work, projects and products at #FIFAfrica17. The exhibition opportunity is free but we encourage a voluntary contribution to enable us ensure that the #FIFAfrica17 experience is as insightful as it is memorable. Please follow this link and let us know your exhibition idea.
#FIFAfrica17 is co-hosted by the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) and the Association for Progressive Communications (APC)
What African Countries Can Learn from European Privacy Laws and Policies
By Edrine Wanyama |
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) came into force in the European Union (EU) in May 2016. The 28 EU member states have until May 2018 to apply the Regulation to existing national laws to ensure the protection of citizens with regard to the processing of personal data and its transfer within the EU and beyond.
In Africa, only 14 countries (Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Mali, Gabon, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Lesotho, Madagascar, Morocco, Senegal, South Africa, Tunisia and Zimbabwe) have enacted data protection and privacy laws. Others, including Kenya, Niger, Nigeria, Tanzania and Uganda, have bills that are yet to be passed into law.
Whereas a continent-wide convention on Cyber Security and Personal Data protection was adopted by the African Union back in 2014, only eight countries (Benin, Chad, Congo, Guinea-Bissau, Mauritania, Sierra Leone, Sao Tome & Principe and Zambia) are signatories and only one (Senegal) has ratified the convention.
Meanwhile, as part of efforts to ensure data protection within the different regional blocs, the Southern African Development Community (SADC) has developed a model law on data protection while as of 2010, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) had the Supplementary Act A/SA.1/01/10 on Personal Data Protection Within ECOWAS. Unlike its regional bloc counterparts in the south and west, the East African Community (EAC) has not adopted legislation on data protection and privacy – it only has a Framework for Cyberlaws which calls for member states to enact laws that protect personal data.
Meanwhile, some of the proposed and existing national laws fall short of comprehensively protecting data and privacy. For instance, Uganda’s Data Protection Bill, 2015 and Ghana’s Data Protection Act, 2012 lack succinct clauses on key areas such as notification of breach and data portability, and also have limitations on the right to access, among others. Despite this, mass collection of personal data continues across the continent, leaving the majority of Africans vulnerable to the violation of their data privacy.
This contrasting state of affairs formed part of the discussions at a July 2017 convening of lawyers, government officials, civil society representatives, academics, and students at the Institute for Information Law at the University of Amsterdam for a five-day training course on issues pertaining to privacy and data protection law relate to the internet and electronic communications.
For over 60 years, the European Convention on Human Rights (1950) has functioned as the framework to guarantee the right of privacy for private and family life. More recently, the European Charter of Fundamental Rights, 2000 has reinforced this right. These instruments are the basis of the robust protections provided for under the GDPR. In Africa similar frameworks which address privacy are less than 15 years old, such as the Declaration of Principles on Freedom of Expression in Africa (2002) (Part V), the Resolution on the Right to Freedom of Information and Expression on the Internet in Africa – ACHPR/Res. 362(LIX) 2016, and the civil society led African Declaration on Internet Rights and Freedoms.
However, where European instruments have been largely endorsed and supported by member states, many African instruments still struggle to gain similar recognition by member states. As in the EU, African countries need to uphold the principles laid down in these instruments towards the recognition and enforcement of citizens’ right to privacy and data protection.
Further, per the GDPR, European states are required to establish Data Protection Authorities (DPAs) to ensure that safeguards are in place to protect user data including across different jurisdictions. African states should embrace similar measures to guard against infringement on citizens’ privacy.
Data Protection Authorities are mandated to independently monitor, raise awareness, handle complaints and conduct investigations, among others, to uphold personal data protection.
Overall, the course highlighted the need for a robust privacy regime across the world to ensure that citizens enjoy due protection of their online data. It also highlighted the need for more efforts in citizen sensitisation on data protection and privacy alongside better frameworks in the African context to support these rights.
CIPESA participated in the course together with representatives from Ohio State Moritz College of Law and Capital University Law School; Global Privacy Practice, Covington & Burling; Institute for Information Law, University of Amsterdam; Berkeley Center for Law & Technology, UC Berkeley School of Law; Dutch Data Protection Authority; and the Washington University Law School, among others.
There are lessons for Africa to learn from the European experience, including the establishment of state and regional mechanisms that strengthen data protection frameworks. However, it is integral that more African countries enact data protection laws, and for countries that have with this law, it should be implemented with oversight from independent bodies as more user data is generated and stored online.
Promoting Youth Participation in Governance Through ICT in Kenya
By Tracy Kadesa |
Youths have emerged at the forefront of online activism and citizen journalism in Kenya. During a December 2016 to March 2017 strike by doctors, young doctors shared their grievances online, ranging from lack of resources in government hospitals to inadequate staffing and poor compensation. One of the stories was that of Dr. Ouma Oluga, the secretary general of the Kenya Medical Practitioners, Pharmacists and Dentists Union, who shared how he had to perform a caesarean section using a torch on his mobile phone due to a power outage. He was only 27 at the time.
Ahead of Kenya’s elections scheduled for August 2017, there have been increased calls for young Kenyans to participate in related processes and vote as a means of positively influencing concerns such as the high rates of unemployment. According to a 2016 World Bank report, Kenya has among the highest youth unemployment rates in Africa.
Against this background, on May 9-10, 2017, the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) convened 30 youth and civil society activists to explore rights and responsibilities, as well as effective and secure ways to engage in the country’s governance processes including through ICT.
The workshop raised awareness about various ICT-based initiatives that have given Kenyan youths an opportunity to regularly discuss issues and analyse the manifestos of candidates running for elective posts. For instance, SiasaPlace runs weekly Twitter chats using #SiasaWednesday with the aim of amplifying women and youth voices. Siasa Place is a hub and co-working space that is passionate about engaging youth and women on civic agency.
Tribeless Youth is another vibrant movement that uses Twitter to engage youth in governance. Ongoing discussions facilitated by #TribelessYouth include #MeetTheNewCandidates where first-time political candidates, mostly youthful ones, are given an opportunity to present what they plan to deliver if elected come August.
Other youth-led initiatives that participated in the workshop included Fatuma’s Voice, a youth empowerment organisation, and Centre for Public Engagement & Social Economic Affairs Kenya (CPESEAK), which works on promoting youth participation in social accountability. Irungu Houghton of Society for International Development; Kenya Dialogues Project (KDP) participated as guest speaker and highlighted KDP’s commitment to advancing youth leadership in Kenya.
The workshop also explored government efforts to motivate the youth to participate in the August 2017 general elections through an initiative dubbed Y-VOTE (Youth Vote). The initiative spearheaded by the Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC) in partnership with the International Foundation for Electoral systems (IFES) leverages social media and on-ground activations to mobilise 18-29 year olds to vote come August 8. The campaign was launched on June 20, 2017 and run to late July.
Participants in the workshop explored ways of leveraging the various civic agency and elections-related initiatives to exercise their rights but also champion a peaceful electioneering period through online activism. Furthermore, discussions entailed digital safety tools and practices to facilitate secure communications.
The participants agreed that they were “no longer leaders of tomorrow but of today” and it was therefore their duty to zealously participate in governance processes towards improved livelihoods. See more insights in video below.
The youth in governance in Kenya workshop was organised in the context of the ICT4Democracy in East Africa initiative which is aimed at leveraging ICT to promote civic participation, democratic governance and respect for human rights.
CIPESA Engages Ugandan Members of Parliament on Implementation of Access to Information Law
By Loyce Kyogabirwe |
It is 12 years since Uganda passed an access to information law with the purpose of promoting transparency and accountability in all organs of the state by providing the public with timely, accessible and accurate information. The law also empowers the public to scrutinise and to participate in government decisions. However, the law has remained largely unimplemented as many Ministries, Departments and Agencies (MDAs) ignore citizens’ requests for information and rarely release information pro-actively, which contravenes the law.
“I have sent several information requests to the Ask Your Government (AYG) Uganda portal. It is now three months and I have never received any feedback,” said Cuthbert Abigaba, Member of Parliament (MP) for Kibaale county in Kamwenge district, while speaking at an engagement of Uganda’s MPs on implementing the Access to Information Act 2005. Organised by the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) on July 13, 2017, the convening was a follow up on an earlier engagement with the MPs on their duties and responsibilities in enforcing the access to information law.
Section 43 of the Access to Information Act requires parliament to receive annual reports from each minister detailing all requests received from citizens for access to records or information, and indicating whether access was granted or not, and where access was not given, the reasons for the denial.
However, Parliament has never received any such reports, nor has it asked ministries to comply with this provision of the law. This issue was also raised earlier in April 2017 when CIPESA presented a position paper on the State of Access to Information in Uganda to MPs on the ICT Committee. The paper highlights some government initiatives to promote access to information, identifies gaps in the law, and makes recommendations for amendments to the law in order to enhance citizens’ access to information.
At the this month’s meeting, CIPESA presented to 16 MPs a comparative analysis of access to information legislation in East Africa and urged the lawmakers to pursue the proposed amendments so as to align Uganda’s law with progressive provisions in some of the East African Community (EAC) Member States’ laws, as well as to international human rights instruments.
“While it is recognised that the EAC region is progressing in promoting the right to information, there are a number of issues that have bottlenecked citizens’ right to information. These include: lack of access to information by non-citizens in Uganda, Kenya and South Sudan; lack of ATI regulations in Rwanda, Kenya, Tanzania and South Sudan; lack of a clear definition of security information by Uganda; lack of provision for transferability of requests in South Sudan; limited scope of bodies the law applies to in Uganda; prohibitive access fees in Uganda, as well as the lack of clear complaints mechanisms in Uganda.” Comparative Analysis of Access to Information Legislation in Africa, June 2017.
During the meeting, the MPs expressed concern over insufficient knowledge among legislators about their duties and responsibilities under the law. They also noted that citizens were not sufficiently aware of their rights and the obligations of public officials. The legislators called for wider awareness raising to increase citizens’ demand for information. “If a Member of Parliament like me did not know the access to information law, what about the citizens who are not even educated?” said Rose Mutonyi, MP for Bubulo West, Manafwa district.
On the other hand, the MPs appreciated the recommendations and proposed amendments contained in the two position papers and suggested an action plan for meaningfully implementing the access to information law. Among the strategies put forward was to engage the Office of the Speaker of Parliament, sensitise more MPs to demand for annual reports from ministers, and engage ministers to submit the annual reports.
Nonetheless, the MPs cited the need for more capacity building on access to information for the majority of legislators to inform their discussions in parliament. As noted by Majegere Kyewalabye, MP for Bunya East, Mayuge district, “We need to be prepared more before we can go on the floor of parliament to present these issues.”
The engagement with MPs was organised by CIPESA in partnership with the Greater Parliamentary North Forum in the context of the ICT4Democracy in East Africa initiative’s objective to engage stakeholders on supportive policies and practices for human rights and democratic governance in East Africa.