By Small Media |
Over the past decade, East Africa has seen a tremendous boom in connectivity and online participation that is beginning to transform the way that citizens across the region communicate, express themselves, and establish communities. In a similar manner, the growth of internet access in the region is beginning to empower civil society organisations (CSOs) to engage with the public, share information, and advocate for citizens’ rights in sometimes challenging and closed political environments. Although the internet offers opportunities to advocates, it also offers the possibility for regional state and non-state actors to interfere with their work, surveil them, and censor their voices.
In this report Small Media, the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA), DefendDefenders, and Strathmore University’s Centre for Intellectual Property and Information Technology Law have sought to map out the state of internet freedom in East Africa, and assess the extent to which ongoing challenges have impacted negatively upon the work of civil society actors in the region. Although we were not able to map out the state of internet freedom across the entire region, we were able to focus our efforts on some of the lesser-studied digital landscapes – Burundi, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania and Uganda.
To measure the state of internet controls in the region, we have taken the African Declaration of Internet Rights and Freedoms (ADIRF) as our key point of reference. This declaration – drafted and signed by a large array of African civil society organisations in collaboration with global internet freedom organisations – establishes a set of rigorous principles by which governments and other stakeholders must abide in order to guarantee the online rights and freedoms of citizens across Africa.
Over the course of this research, we have found that there is an urgent need for East African civil society to be given support to improve their digital resilience in the face of growing threats of surveillance and censorship across the region. In all of the countries surveyed in this report, CSOs failed to demonstrate a baseline of digital security knowledge, or else failed to implement practices effectively.


At the same time, we found that governments across the region require support to bring their policies into compliance with the principles of the African Declaration on Internet Rights and Freedoms – a set of principles developed by African internet freedom stakeholders to guarantee a free and open internet in Africa.

Small Media, CIPESA, Defend Defenders and CIPIT hope that this research can help to support the security of civil society actors, empower activists to support the principles of the African Declaration, and press their governments to adopt it.
Read the full report here.
"What Must Change?" For More Gender Equality Online
Storify |
This International Women’s Month, we reflect on what presently shapes women’s participation in the online arena. On International Women’s Day, 8 March, we hosted Akina Mama Wa Afrika, Women of Uganda Network (WOUGNET), Connecting Voices of Citizens (CVC) and the Ask Your Government (Uganda) online portal in an online Twitter chat during which we asked “What must change?” to enable a more inclusive online community which recognises gender equity.
See some highlights from the chat here
Internet Freedom Festival 2017: CIPESA to Host Session on Navigating Internet Freedom Challenges in Africa
By Lillian Nalwoga |
The annual Internet Freedom Festival (IFF) has commenced in Valencia, Spain with hundreds of journalists, activists, technologists, policy advocates, digital safety trainers, and designers from around the world in attendance. The Collaboration on International ICT policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) will host a session “Internet Freedom in Africa: Navigating the challenges” to spark conversation on current internet freedom challenges in Africa while providing possible solutions. In addition, CIPESA shall join panel sessions hosted by partners, such as the Association for Progressive Communications (APC), Hivos, the Ford Foundation and International Media Support (IMS).
The IFF is built upon the goals of creating an inclusive information and resource sharing space, increasing the diversity of the internet freedom community, and collectively improving the services, strategies, and tools offered to the most vulnerable individuals by mapping censorship, surveillance and access obstacles faced in different regions in the world.
As internet usage rises in Africa, so do the abuses and attacks on online rights fuelled by the proliferation of laws which negate the rights to privacy and freedom of expression. Further, limited judicial oversight over surveillance and interception of communications are contributing to self-censorship and threatening civic participation and free flow of information online.
The ethos of the IFF resonates with CIPESA’s areas of the work. These include monitoring online rights violations and information control tactics, championing a network of actors in Africa to advance progressive policy development and multi-stakeholder engagements and capacity building on digital skills among human rights defenders and journalists. The session we shall host on navigating internet freedom challenges in Africa will partly be informed by CIPESA’s report on the State of Internet freedom in Africa 2016 and issues that are influencing the right to information, data privacy and free speech online in Africa. We will also explore the lessons learnt from researching and advocating for internet freedom in various African countries.
The session will offer participants an opportunity to interact with internet freedom thought leaders from Africa by exploring two key questions:
- What is the status of internet freedom in Africa?
- How can we ensure a sustainable approach in promoting a free, open and safe internet in Africa?
Join us Friday March 10, 2017 09:45 – 10:45am in the Visual Room or contribute to the conversation online: #InternetFreedomAfrica @cipesaug @opennetafrica
Other sessions at IFF of interest to CIPESA, some of which shall feature CIPESA staff, include:
- Promoting the African Declaration on Internet Rights and Freedoms, organised by APC.
- Side Dish Regulation: Catching up with Regulation of Internet outside the mainstream, organized by Paradigm Initiative Nigeria (PIN). CIPESA participating on the panel.
- Practical implementations of human rights respecting cybersecurity policy, organised by APC.
- Bridging the localization gap: digital security tools for everyone, organised by IMS. CIPESA participating on the panel.
- Case study: Understanding internet censorship in Africa’s repressive environments through the deployment of OONI software probes and Citizen Lab mixed research methods, organised by CIPIT, Strathmore University.
- Ford Foundation research meeting. CIPESA participating on the panel.
- Celebrating Gender Campaigns in the Global South, organised by APC and AccessNow.
Look out for our session at #InternetFF on #InternetFreedomAfrica: Navigating The Challenges >> We have an exciting lineup of panelists! pic.twitter.com/CyB2DXyXhz
— CIPESA (@cipesaug) March 2, 2017
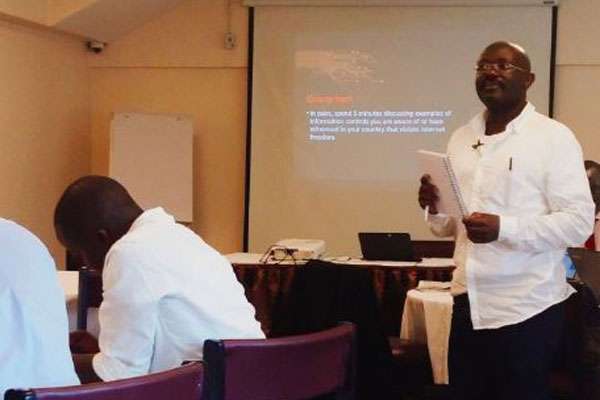
Lobby Calls For Internet Freedom, Urges Responsible Use Of Social Media
By Lillian Mutavi |
Photo: The Collaboration on International Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) executive director Wairagala Wakabi makes his presentation on internet freedoms in Kenya on January 27, 2017. Lillian Mutavi | Daily Nation Media Group
This article was originally published in the Daily Nation
13 Days Later, Cameroon Maintains Internet Shutdown Despite Global Outcry
By Juliet Nanfuka |
An internet shutdown in the primarily Anglophone regions of north-west and south-west Cameroon is now in its 13th day. The shutdown was first initiated across the country on January 16 and on January 17, internet access was reinstated in the Francophone parts of the country. As of January 30, the blockage in the Anglophone regions including in key towns such as Buea and Bameda remains in pace.
The shutdown was imposed in the wake of ongoing strikes, fatal violence and protest action against the continued “francophonisation” and marginalisation of English speakers who say that “the central government privileges the majority French-speaking population and eight other regions.” Cameroon’s constitution recognises the two languages as equal and calls for bilingualism. Further, the arrest of the activist leaders of the Cameroon Anglophone Civil Society Consortium, Nkongho Felix Agbor Balla and Fontem Neba, have done little to address the perception that government is trying to silence voices of dissent.
Critics of the shutdown have called the shutdown a violation of “citizens’ rights to freedom of expression and access to information”. On January 22, civil society organisations from around the world sent an open letter to the President of Cameroon, and the ministers for telecommunications and communication urging an immediate end to the shutdown. No response has been received.
Indeed, there has been global outcry on the shutdown which has affected the livelihoods of millions of citizens in the affected regions. Mobile Money services providers, microfinance Institutions and banks have also been affected, forcing residents to travel to Francophone towns like Douala to conduct their financial transactions (Listen to iAfrikan podcast).
In the days leading up to the shutdown, the Ministry of Post & Telecommunications (MINPOSTEL) issued a directive to operators to send out messages warning subscribers against the “bad” use of social media. Operators received backlash on social media for sending the government-directed message which was seen to encourage self–censorship.
However, Philisiwe Sibiya, CEO at MTN Cameroon, argued that the communication was not intended to “curtail customer rights and violate customer privacy.” She explained that the regulator, MINPOSTEL, “may from time to time request telecom operators to carry messages on their networks intended for the general public. This was the case recently when MTN Cameroon, along with other operators, broadcast a message from MINSPOTEL regarding the use of the internet.”
“Dear subscriber, publishing as well as spreading false news,including on the social media, are punishable by the Penal Code and the law
Communiqué sent to users of Camtel, MTN, Orange, Nextell mobile telephone lines from MINPOSTEL
Back in November 2016, the government launched a campaign against social media, calling it “a new form of terrorism”. At the time, Facebook and Twitter users were sharing information, including pictures, about a train derailment in which 80 people died while government maintained silence about the accident.
Whereas language as the basis for an internet shutdown is new, the practice has become common in Africa particularly during political unrest (Burundi), elections and inauguration (Uganda), economic failure (Zimbabwe) and exams (Ethiopia).
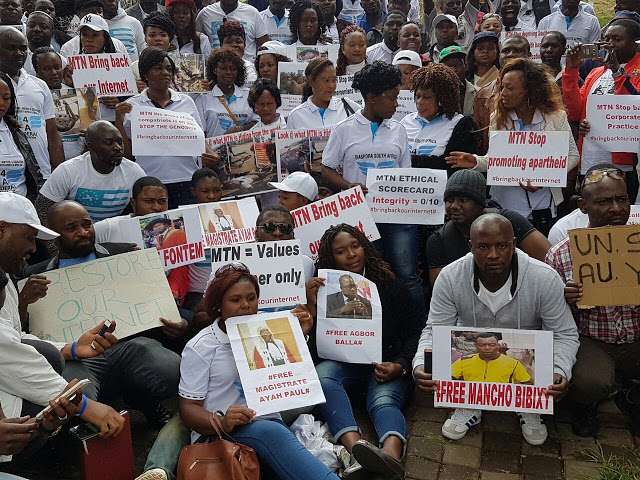
Various campaigns are underway calling for the Cameroon Government to reinstate internet access, including this Use your voice! Tell Cameroon to turn the internet back on and the hashtags #BringBackOurInternet #KeepItOn.
See this Aljzeera discussion titled Is Cameroon persecuting its English speakers? It features Elvis Ngolle Ngolle – Former Minister of Special Duties in the Office of the President of Cameroon. Julie Owono – Head of the Internet Desk at Internet Without Borders and Albert Nchinda – Political Analyst.
Image: Cameroonians in South Africa gathered at the MTN Headquarters in Johannesburg to protest the shut down of internet in its English-speaking regions of Cameroon.
Source: Kinnakas Blog