By Nadhifah Muhammad and Tendo Racheal |
Imagine running a business in today’s fast-paced digital world, where almost everything from customer data, marketing to financial transactions happening online. Now, imagine having little or no knowledge on how to protect that data, relevant laws and regulations or worse, unknowingly violating digital rights. That is the reality for many businesses in Uganda today.
Data protection, data privacy, cybersecurity, and surveillance are not just techy buzzwords, they’re essential to building a safe and inclusive digital economy. Yet, many small and medium enterprises (SMEs), which account for 90% of Uganda’s private sector, either do not fully understand responsible digital practices or lack the tools to do so.
That’s where the Advancing Respect for Human Rights by Businesses in Uganda (ARBHR) project comes in. With support from Enabel and the European Union, the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) is co-implementing this project which seeks to reduce human rights abuses connected to business activities in Uganda, particularly those impacting women and children.
Among others, CIPESA is working to raise awareness on digital rights in the business context. As businesses increasingly rely on digital technologies to operate and innovate, their role in upholding digital rights becomes paramount. Yet many Ugandan businesses, particularly SMEs, lack a comprehensive understanding of digital rights principles and their obligations in upholding them.
Early this year, CIPESA published a call for applications to the Civil Society (CSO) Fund for entities interested in championing digital rights in the business sector. Six CSOs were selected under the competitive process and, together with four innovation hubs, SME, employer and employee associations, will be supported to implement awareness-raising activities. These include Evidence and Methods Lab, Boundless Minds, Wakiso District Human Rights Committee, Media Focus on Africa Uganda, Girls for Climate Action, Recreation for Development and Peace Uganda, Private Sector Foundation Uganda, Federation of Uganda Employers and The Innovation Village.
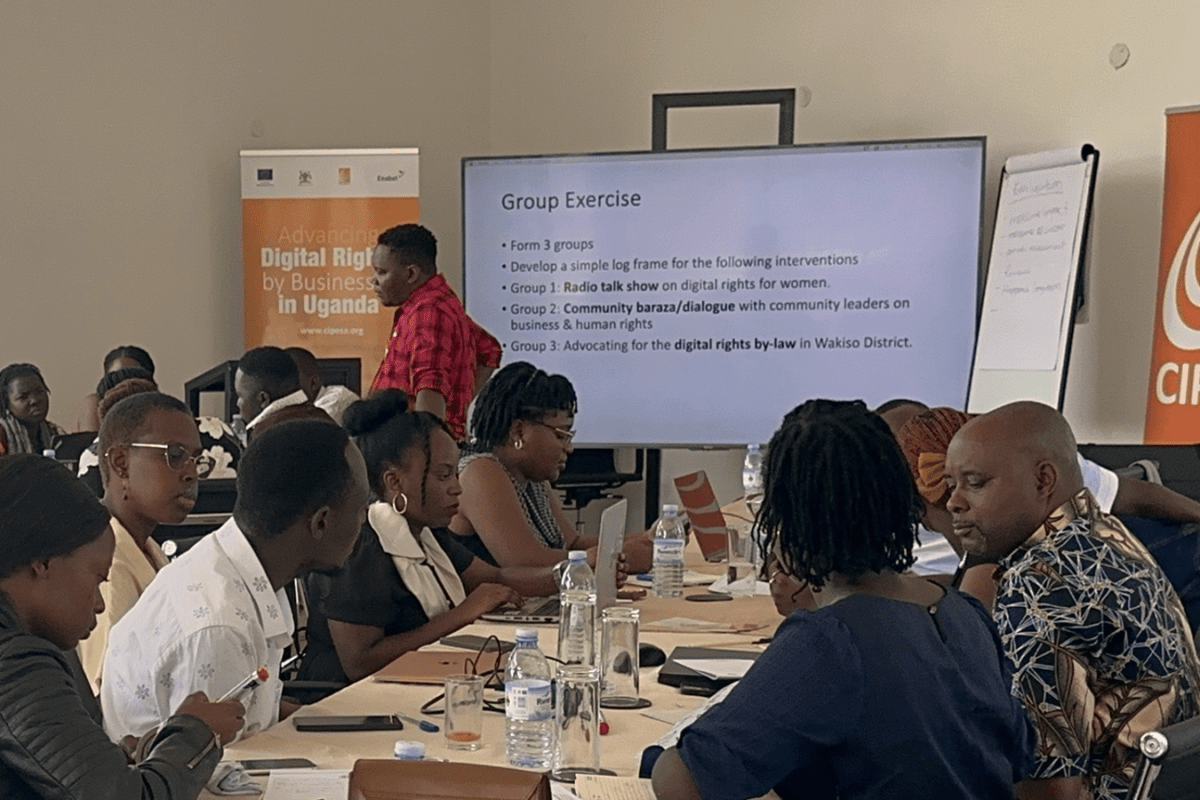
To ensure that the partners effectively undertake their interventions, CIPESA convened a three-day bootcamp on March 4–8, 2025 aimed at enhancing their knowledge and skills in implementing awareness raising and advocacy campaigns as part of advancing the business and human rights agenda. The bootcamp brought together 35 participants.
Key topics of discussion included Trends in Business and Digital Rights in Uganda, such as Privacy and Data Protection, Cybersecurity, Inclusion and Labour Rights; Impact Communications and Storytelling for Awareness and Advocacy; as well as Digital Content Creation.
The discussions were framed under the Uganda National Action Plan on Business and Human Rights (NAPBHR), which seeks to protect human rights, enhance corporate digital responsibility to respect human rights, and ensure access to remedy for victims of human rights violations and abuses resulting from non-compliance by business entities in the country.
The project is very timely to create more awareness on business and human rights issues especially in regards to labour rights, effective redress mechanisms for BHR [Business and Human Rights] violations and engendering of digital rights. – Training Participant
Uganda’s ARBHR aligns with the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs), which outline the corporate responsibility to respect, protect, and remedy human rights abuses in business operations. By equipping businesses with the knowledge and tools to integrate digital rights into their policies and practices, the ARBHR project is contributing to a global movement that ensures businesses operate ethically, respect fundamental freedoms, and uphold human dignity in the digital space.
For Uganda’s business sector to thrive in a digitally connected world, businesses must align with these principles, creating a culture where human rights are not an afterthought but a core business responsibility.
Therefore, as partners roll out their awareness raising action plans over the next eight months, it is envisaged that over 200,000 individuals will be reached in the regions of Albertine, Busoga and Kampala Metropolitan. Through radio talk shows, skits, social media campaigns, community meetings, capacity building trainings, visualised Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) products, and digital clinics, these stakeholders will have enhanced appreciation of digital rights protection to foster a more informed and active community of advocates for rights-respecting practices among businesses in Uganda.
So, if you’re a business owner, a CSO representative, or just someone passionate about digital rights, this is your chance to be part of something bigger. Join the conversation, and let’s build a digital future we can all trust.