By David Sullivan |
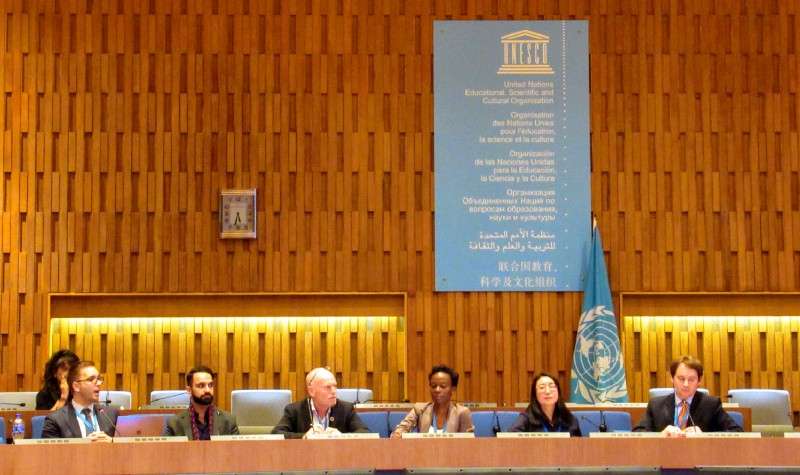
Few events bring together the multitude of actors with a stake in tough technology and human rights challenges quite like the Internet Governance Forum, or IGF. The 2018 edition, held in Paris and hosted by UNESCO, was no exception, with nearly 2,000 delegates from 143 countries. It was a particularly suitable setting for the Global Network Initiative, or GNI, to
gather a panel of experts to reflect on the alarming trend of government-ordered network disruptions.
Collaborating with the Open Internet for Democracy Initiative, GNI brought members and experts from civil society, the private sector, and international organizations together to consider challenges and opportunities for the movement fighting network disruptions. Session moderator Daniel O’Maley from the Center for International Media Assistance opened the conversation by noting that disruptions are increasing worldwide, affecting both democracies as well as authoritarian countries. With this prompt, the speakers highlighted successful advocacy initiatives and shared their insights into this concerning trend.
Usama Khilji from Pakistani civil society organization Bolo Bhi described how network disruptions have become normalized in many societies, with an increasing expectation that connectivity will not be available around events like public holidays or political protests. He said there is little evidence that the use of network disruptions and shutdowns during sensitive moments is effective at providing security for citizens and stressed the importance of making this point with policymakers.
Providing a company perspective, GNI Board member Patrik Hiselius from Sweden’s Telia Company described tools that help companies contend with “unusual requests” such as disruption orders. Telia has a form they use to assess risks and escalate such requests, ensuring senior company officials are informed and reducing security risks for staff on the ground. He also highlighted GNI’s one-page guide on the negative consequences of shutdowns, a document that arose out of a brainstorming session at the 2016 IGF and which has now been translated into 12 languages.
Ashnah Kalemera from the Collaboration on International ICT Policy in East and Southern Africa, or CIPESA, discussed their work documenting the economic impact of disruptions on the African continent, which was used successfully in advocacy to prevent shutdowns in Ghana and Kenya and to strengthen partnerships with the private sector and technologists.
Representing our hosts at UNESCO, Xianhong Hu described network disruptions as a threat to Internet universality and suggested the indicators they have been developing may be a useful tool for documenting and discouraging such actions.
Lastly, participating remotely from Cameroon and persevering through technical difficulties, entrepreneur and activist Kathleen Ndongmo said that governments who shut down the Internet are not only blocking democracy but also costing their societies millions of dollars in lost business. She urged the audience to collaborate at the regional level to push for the passage of legislation that protects rights and innovation, such as Nigeria’s Digital Rights and Freedom Bill.
The audience contributed to the discussion with probing questions and comments, from how strategic litigation may contribute to the fight against disruptions to a reminder of the significant privacy risks from surveillance in many settings when networks remain on.
The discussion left me reflecting on more than two years of work by GNI to build consensus among our members and with policymakers on this issue. Early on, we faced challenges bridging very different perspectives and postures among human rights NGOs and telecommunications and Internet companies. Through discussion and deliberation, we reached consensus on a common position in 2016. Since then, we have developed tools and conducted research, convened experts and affected communities, and brought the digital rights and technology policy communities into alignment as powerful voices. But network disruptions are blunt instruments that affect a far wider population than just the technology industry. We need to marshal a much broader movement, one including the media, labor unions, and a wider set of sectors, to demonstrate the consequences of government-ordered shutdowns and educate policymakers about alternatives.
In his rousing opening address to the IGF, UN Secretary-General António Gutteres said “we must be more than multistakeholder, we must also be multidisciplinary,” and he went on to “urge your digital discussions to move beyond the so-called ‘usual suspects’.” Following his lead, we need a concerted effort to forge greater and new alliances, between both online and offline communities, if we are to keep free and open networks connected around the globe.
This article was first published on November 29, 2018 on GNI Website.