By Hilda Nyakwaka |
The Forum on Internet Freedom in Africa event this year was hosted in Addis Ababa between 23rd and 26th September. This event was considered monumental because a few months prior, there were internet shutdownsand this was a testament to the progressive strides Ethiopia was making in creating an open and accessible internet for its citizens.
The first two days of the week were dedicated to a training on the Universal Periodic Review (UPR) hosted by Small Mediaand Data4Changeand with representatives from over 10 African countries.The UPR, an innovation by the UN Human Rights Council, is a periodic review of the human rights records by the 193 member states of the UN (UPR). The main purpose of this training was to see how to champion for digital rights at the coming UPR.
Over these two days participants went over different concepts such as the importance of making recommendations to countries through the UN in an effort to improve the digital space, how to build capacity for recommendation-making processes, how to increase participation in the UPR process and how to foster collaborations between participants from different countries.
Some common concerns that the participants shared about the previous UPR cycles included the focus of civil society organisations on report writing as opposed to lobbying, lack of accessibility to stakeholder reports by diplomats and other concerned citizens and the lack of focus on digital rights and other human rights when making recommendations.
Some of the key takeaways were the toolsbuilt by Data4Change to guide interested parties in creating advocacy strategy plans. These tools help users to not only see what recommendations have been made to their countries of interest, but to also discover and fill the gaps in the recommendations made and which countries would be important to partner with. During this session, all participants were able to make and rate each other’s recommendations to their individual countries with specific attention to digital rights.
There was also a general agreement to increase local stakeholder mobilization, awareness workshops, jointly documenting abuse of digital rights so as to have greater impact and lastly to properly document all our work. At the end of the training, we were all awarded certificates of completion for attending the trainings and completing online courses pertaining to the UPR process.
The next two days marked the official start of the forum, which was open to everyone who had registered to attend. There were several panel sessions occurring simultaneously focusing on different internet issues across Africa. The opening panel was attended by H.E Dr. Getahun Mekuria, the Minister of Information and Technology in Ethiopia who reiterated the government’s plans to liberalize the telecommunications industry in Ethiopia and to reduce cases of shutdowns in a move to increase and improve the citizens’ access to the internet.
Sessions that I was particularly interested in narrowed, their focus to how marginalized and targeted communities interact with technology and some of the solutions they have adapted to their situations.
One such session was on the importance of African feminist movements in improving women’s voices in the digital space as moderated by Rosebell Kagumire, an award-winning blogger and Pan-African feminist . In this session, feminists from across the continent reiterated the ways in which offline patriarchal systems were replicated online against women. One point that resonated with most attendees was that women were still being policed and bullied out of a lot of social apps such as Twitter and most women preferred to be invisible. Cases were brought up on how hypervisible women were facing a lot of challenges.
In addition to this, there was also a celebratory moment when the panelists mentioned some of the movements that succeeded in championing for women’s rights both offline and online some as big and visible as the #TotalShutdownKE that fought against femicide in Kenya and the revolution in Sudan that had women at its forefront and which gained support from across the world. A major gap that was identified in this conversation was the need for building more local movements and having inclusivity within the movement to include women from the LGBTQI community as their online experiences were unidentified despite being equally important.
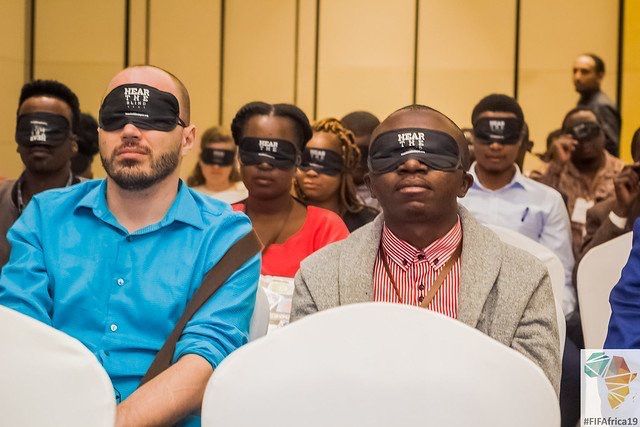
Another key session was held on technology and disability where persons living with disabilities spoke about how to use ICTs to reduce accessibility barriers. Some of the challenges the panelists included insufficient ICT training, lack of accessibility features on even the most basic layouts of sites and apps, affordability of devices with accessibility features as one of the panelists cited that a mobile phone with accessibility features would cost one $800 which most Africans both abled and disabled cannot afford comfortably.
An Ethiopian Case Studywas used to explain just how crucial and important it was to provide holistic education and inclusive support to people living with disabilities within our communities. Some of the solutions that the panelists offered up to improve accessibility included proper policy implementation and strict punitive measures for those who failed to implement any policies, being intentional by teaching about accessibility features right from software development classes at the college level and putting a cap to funding that requires companies and organizations to provide opportunities for and hire people living with disabilities in their firms and provide ample accessibility features before receiving full funding. There was also a call to create awareness campaigns to make citizens aware of the challenges that a large section of our communities experience and how to develop protection mechanisms for them.
In conclusion, FIFAfrica 19 was a great opportunity to share experiences and solutions to challenges we as Africans seem to be experiencing when it comes to digital rights and internet freedom. In case you weren’t able to join us in Addis for this edition of FIFAfrica, find herethe agenda for the forum, somelive tweets from the event and the report on the State of Internet Freedom in Africaby CIPESA, launched at the forum.
Working Towards Universal Internet Access and Digital Equality in South Africa
By Izak Minnaar |
“All South Africans – and especially those who cannot afford it and other vulnerable groups – need a daily first tranche of free internet access to exercise their basic human rights such as access to government services, participating in the digital economy, looking for jobs, online communication and for learners and students to access online educational resources. This is the only way to achieve universal access to information and digital equality amongst our citizens, including the rural poor who have access to mobile phones.”
This is the call made by the South African online and media industry bodies, the South African National Editors’ Forum (SANEF), the Interactive Advertising Bureau South Africa (IABSA) and Media Monitoring Africa (MMA), with the support of the Association for Progressive Communications (APC), an international network of human rights organisations and advocacy groups for access to information.
At the 2019 International Day for Universal Access to Information (IDUAI) commemoration in Pretoria, they expressed the need for a national effort to coordinate existing legislation, policies and initiatives to provide citizens with a basic level of universal free internet access, coinciding with the launch of a report titled Universal Access to the Internet and Free Public Access in South Africa.
The group noted that while the South African government has made domestic and international commitments to take steps towards achieving universal access to online information, these commitments cannot be achieved without providing for a level of free access, in particular for disadvantaged and marginalised groups who would otherwise not be able to enjoy internet access.
The report proposes a seven-point plan which will assist the government with proposals to take steps towards progressively realising a basic level of universal free access to online information, both within the government itself and through engagements with private entities and other stakeholders.
 The proposed plan endeavours to provide a comprehensive approach to universal and free internet access, from the gradual introduction of free municipal wifi as a basic service and access at other government sites, underpinned by a set of standards for free access, to digital literacy programmes. Full details of these proposals are captured in the report.
The proposed plan endeavours to provide a comprehensive approach to universal and free internet access, from the gradual introduction of free municipal wifi as a basic service and access at other government sites, underpinned by a set of standards for free access, to digital literacy programmes. Full details of these proposals are captured in the report.
The universal internet access proposals are part of a three pronged approach to achieve the objectives as set out in the SA Promotion of Access to Information Act (2000), to “actively promote a society in which the people of South Africa have effective access to information to enable them to more fully exercise and protect all of their rights”
First, it must be made easier for citizens to use the Promotion of Access to Information Act (PAIA) to access information. A major improvement in the law will be to make provision for pro-active disclosure of information, as prescribed by the African Model Law on Access to Information, published by the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights in 2013. A major review and update of PAIA is required, beyond the current process to add clauses on party funding.
The second issue – and a logical consequence of pro-active disclosure – is for information holders and access to information activists to vigorously pursue the open data and open government agenda. As a founder member of the United Nations initiated Open Government Partnership (OGP), the South African government has already made ambitious commitments to establish open data portals, with projects ranging from Open Justice, Open Budget (such as the Vulekamali and Municipal Money data portals) and Open Elections, all of which are in different stages of implementation. However, South Africa still needs to deliver on a number of commitments made in its OGP National Action Plan.
With all this information available online, the third requirement to ensure “effective access to information” as PAIA requires, is to provide universal access to the internet. In 2016 the African Commission on Human and People’s Rights called on African governments to take legislative and other measures “to guarantee, respect and protect citizen’s right to freedom of information and expression through access to internet services”.
A 2017 APC Issue Paper initiated by the same group of online and media organisations, titled Perspectives on Universal Free Access to Online Information in South Africa: Free Public Wifi and Zero-Rated Content lists South African legislation and polices dealing with the need for citizens to have the means, capacity and skills to fully participate in a digitally driven democracy and economy, in line with the vision expressed in the National Development Plan of universal access to the internet and an e-literate public.
The seven-point plan is an effort by the online and media industry bodies to provide government and industry with practical plans to implement the existing legislation and policies.
This presentation provides an overview of the seven-point plan and was shared at the Forum on Internet Freedom in Africa 2019 (FIFAfrica19) which was held in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
An Enabling Environment for Inclusive Digital Transformation
FIFAfrica19 |
The digital economy, including cross-border services, digital trade, and electronic commerce (eCommerce), contributes to democratic and economic development by expanding market access for local businesses, promoting inclusive trade, creating jobs, and expanding tax revenue for governments to provide essential services. As the scope of digital innovation expands around the continent, so must national and regional priorities and policies align to facilitate greater competitiveness, inclusiveness all while respecting online freedoms and digital rights.
This panel discussion will feature key insights on priority policies and initiatives gleaned from the FIFAfrica pre-event hosted by the Center for International Private Enterprise (CIPE). On September 24, CIPE will host a policy roundtable with public, private, and civil society stakeholders from across the continent to discuss regional opportunities for inclusive economic and entrepreneurial development in an increasingly digital future. Topics from the policy roundtable include: data flows and privacy, eCommerce and eTrade, e-payments and financial inclusion, and the future of entrepreneurship.
Following FIFAfrica, proposed initiatives and policies identified in the policy roundtable discussions and in this panel will be shared with the digital rights community and the public.
Moderator: Louisa Tomar, Global Program Officer, CIPE
Panelists
- Peter Mwencha | Africa eTrade Group, Kenya
- Representative | CIPESA
- Grace Githaiga | KICTANet, Kenya
- Representative | MINT, Ethiopia
Follow the conversation using #FIFAfrica19 and #InternetFreedomAfrica.
Overview of Cameroon’s Digital Landscape
By Simone Toussi |
The Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector in Cameroon has evolved considerably since 2010, despite the persistence of the digital divide and affronts to freedom of expression online. The country’s digital landscape was boosted by the launch in May 2016 of the National ICT Strategic Plan 2020, which recognised the digital economy as a driver for development. The country has registered increased investments in telecommunication and ICT infrastructure, including extension of the national optical fibre backbone to about 12,000 km, connecting 209 of the country’s 360 sub-divisions, and neighbouring countries such as Chad, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, the Central African Republic and Nigeria.
By 2018, the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications reported that mobile phone subscribers stood at 18.8 million representing a penetration rate of 83%, while internet penetration was 35%. There are four big telecommunications service providers in Cameroon – MTN, Orange, Viettel and the state-owned CAMTEL. With 48% of the mobile market share or 8.7 million subscribers, MTN is the leading service provider, according to its report for the first quarter of 2019.
Over the years, Cameroon has scored some improvements in ICT development and affordability. For instance, on the ICT Development Index (IDI) of the International Telecommunications Union (ITU), its value improved from 1.54 in 2010 to 2.38 in 2017 – against the highest global value of 8.98 for Iceland, and between the highest African value of 5.88 for Mauritius and the lowest 0.96 for Eritrea. Cameroon thus ranked at 149 out of the 176 countries assessed, with more than twenty African countries ranked above it. On affordability of the internet, Cameroon’s ranking has also slightly improved – currently ranked 50, up from 53 in 2015, out of 60 countries. This still makes internet access in Cameroon among the most expensive of the countries surveyed.
Meanwhile, internet shutdowns, arrests and intimidation of online critics, and censorship of online content raise concerns about the government’s commitment to nurturing a sustainable and inclusive digital society.
ICT Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
The Cameroonian Constitution provides for freedom of expression, freedom of the press and of communication. It states: “the freedom of communication, of expression, of the press, of assembly, of association, and of trade unionism, as well as the right to strike shall be guaranteed under the conditions fixed by law”.
Relevant agencies governing the sector include the Telecommunication Regulatory Agency (ART), and the National Telecommunications Agency (ANTIC) – both under the mandate of the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications (MINPOSTEL). Other entities such as the Ministry of Communication and the National Council of Communication also has regulatory and advisory roles with regards to media.
These agencies are guided by key laws that govern ICT including Law n° 98/014 of July 14, 1998 governing telecommunications and its amendment of December 29, 2005; Law n° 2010/013 of December 21, 2010 on e-Communications, and its amendment of April 2015; Law n° 2010/012 of December 21, 2010 on Cyber Security and Cybercrime; and Law n° 2010/021 of December 21 2010 governing e-Commerce. Other legalisation related to ICT are the Framework Law n° 2011/012 of May 6, 2011 on Consumer Protection, Law n° 2001 / 0130 of July 23, 2001 establishing the minimum service in telecommunications, and Law n° 98/013 of July 14, 1998 on competition which governs all sectors of the national economy.
The 2014 Law on the Suppression of Terrorist Acts, which was enacted to support the fight against terrorism and growing threats from the jihadist group Boko Haram, has been used as a tool to suppress journalism and opinion critical of the government under the guise of preventing the spread of fake news and threatening national security. In January 2018, the Minister of Justice issued a directive to magistrates to “commit, after clear identification by the security services, to legally prosecute any person residing in Cameroon who uses social media to spread fake news”.
A new law is the 2019 Finance Act, which under Section 8, introduces taxation on software and application downloads produced outside of Cameroon, at a flat rate of 200 Central African Francs (CFA), equivalent to USD 0.34, per download. Whereas the government is yet to issue implementation guidelines for the taxes, once in effect, they will result in additional costs for digital platform users.
Access and Affordability
Article 4 of the 2010 eCommunications law states that every citizen “has the right to benefit from electronic communications services”. The same law establishes a Universal Service Access Fund, aimed at ensuring equal, quality and affordable access to services (Articles 27-29). Whereas internet and mobile telephony have registered growth, access and affordability remain a challenge, especially among rural and poor communities. Currently, the average cost of 1GB of data is 2,000 CFA (USD 3.4) per month, and with the proposed levy of 200 CFAs (USD 0.34) on software and application downloads, costs are expected to further increase. With an estimated per capita income of USD 1,500 in 2018, the prevailing rates are over and above the Alliance for Affordable Internet’s recommendation of 1GB of data costing 2% or less of average monthly income.
Gender Digital Divide
A 2015 report by the Web Foundation found that in Cameroon only 36% of women compared to 45% of men were internet users. The key factors inhibiting women’s access to the internet and digital devices in Cameroon included literacy levels, cost relative to income, access to devices, perceived relevance and usefulness, lack of time and poor infrastructure. Towards addressing the digital gender divide, the National ICT Strategic Plan 2020 states among its objectives the need to “support the development of female skills in the field of digital engineering“, and to “support technological and scientific vocations for women“. However, these objectives are not linked to any specific projects within the plan’s priority action areas.
Meanwhile, without much in the way of provisions for gender, cultural and linguistic diversity, the country’s ICT laws remain largely silent on diversity and inclusion within the ICT sector. Further, seven years since its passing, the Framework Law on Consumer Protection, which includes provisions on consumer rights and quality of services within the technology sector, remains largely unenforced due to the absence of implementation guidelines.
Privacy and Data Protection
Cameroon has no data protection or privacy law. However, the national Constitution amended by the Law N°. 96-06 of 18 January 1996, guarantees privacy of communications in its preamble, stating that “the privacy of all correspondence is inviolate. No interference may be allowed except by virtue of decisions emanating from the Judicial Power”. The 2010 Cybersecurity and Cybercrime law also provides for the privacy of communications under Article 41 and outlaws the interception of communications under Article 44. The obligation for service providers to guarantee users’ privacy and the confidentiality of information is covered under Articles 42 and 26.
According to Article 26(1); “Information system operators shall take all technical and administrative measures to ensure the security of the services offered. To this end, they should be equipped with standardised systems that enable them to identify, evaluate, process and continuously manage the risks related to the security of information systems in the context of services offered directly or indirectly”. However, the law does not specify the guiding principles for the collection and processing of personal data, nor users’ right to access and update such data.
Network Disruptions
The government of Cameroon has in the past initiated two internet shutdowns in the Anglophone region of the country, which together lasted 240 days and drew international condemnation. The shutdowns were imposed in the wake of ongoing strikes, fatal violence and protest action against the alleged “francophonisation” and marginalisation of English speakers who claim that “the central government privileges the majority French-speaking population and eight other regions.” It is estimated that the regional internet shutdown cost USD 38.8 million in addition to affecting access to public services, education, and daily livelihoods.
Guaranteeing an Inclusive Digital Space in Cameroon
Cameroon’s government has professed its intention to leverage the digital economy for sustainable development and to establish an enabling legal and regulatory framework. However, developments such as taxation of application downloads, internet disruptions, and limited efforts to bridge the digital gender divide, indicate a shrinking digital space and are likely obstacles to the uptake of ICT. Efforts are thus necessary to ensure a digital environment that is both open and accessible to all, upholds users’ safety and security, and guarantees constitutional rights. These efforts should include a strengthened legal framework with implementation guidelines to ensure enforcement, compliance monitoring, and accountability.
Moreover, the adoption of a specific law on privacy and data protection is recommended, so as to guarantee the principles of anonymity and consent, and in line with international best practice. For civil society organisations, it is recommended to intensify advocacy against regressive policy and practice including internet disruptions, and the enforcement of consumer protection and universal services. Crucially, civil society should play an active role in policy consultative processes and citizen sensitisation on digital rights and literacy.
Placing ICT Access for Persons with Disabilities at the Centre of Internet Rights Debate in Kenya
By CIPESA Writer |
Persons with disabilities have unique needs and have for long been disadvantaged, yet, the more some African countries get digitally connected, the deeper the digital divide for this community seems to grow. Indeed, debates about internet governance and the inclusiveness of the information society have not prominently featured the needs of persons with disabilities. This, despite Information and Communications Technology (ICT) having the potential to improve the lives of persons with disabilities.
However, it was a different story in Kenya a month ago, with disability rights featuring prominently at the Kenya Internet Governance (KIGF) and being the focus of a multi-stakeholder workshop held the day before the forum.
“ICT for us is an enabler; for a person with disability, ICT makes the world go round,” remarked Erick Ngondi of the United Disabled Persons of Kenya (UDPK), at the end of a workshop organised by the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) alongside the Kenya Internet Governance Week that is spearheaded by the Kenya ICT Action Network, or KICTANet. “For me this has been one of the first meetings as relates to ICT and disability, so this is an excellent move.”
The workshop brought together 28 participants who included representatives of disabled persons’ organisations, government departments, telecom companies, academic institutions, technology companies, civil society organisations, and the media. The workshop explored ICT inclusion obligations for the state and for private companies and discussed what Kenya needs to do so as to improve access and usage of ICT for persons with disabilities. (Watch video with highlights from the meeting.)
“This workshop is one of its kind because it is not only about issues of physical accessibility but also informational and technological accessibility for persons with disabilities. This is a good initiative by CIPESA and I want to applaud them for this. It is a journey that has started and I look forward to us going on with this journey until we achieve our goal of persons with disabilities being included in technology.” George Shimanyula, Cheshire Disability Services Kenya.
In addition, the workshop disseminated a draft tool for monitoring compliance and implementation of ICT and disability rights obligations, including those specified by national laws and the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons With Disabilities (CRPD). The aim was to receive feedback on the tool, and to create awareness of how state and non-state actors can assess the compliance of government departments and private entities with digital accessibility obligations.
Kenya’s constitution is strong on disability rights, outlawing discrimination on the grounds of disability in article 27(4); and providing that a person with disability shall be entitled to treatment with respect and dignity, access educational institutions and facilities, have reasonable access to all places, public transport and information, and access materials and devices including for communications (article 54). Moreover, Kenya’s National ICT Policy of 2016 outlines, under article 13, strategies for “an accessible ICT environment in the country in order to enable persons with disabilities to take full advantage of ICTs.”
https://twitter.com/BakeKenya/status/1156905814122217487
However, as was noted by Judy Okite, founder of the Association for Accessibility and Equality, many of the digital accessibility strategies outlined in the 2016 policy remained unfulfilled. While Kenya’s government is making significant steps to move its services online, the platforms are not favorable to those who are visually imparied. “Are we widening the digital divide by moving our services online? Is ICT recognised as an enabler for PWD in Kenya?” wondered Okite.
The Government will where appropriate take measures to:
(a) ensure that ICT services and emergency communications made available to the public are provided in alternative accessible formats for persons with disabilities (PWD);
(b) review existing legislation and regulations to promote ICT accessibility for PWDs in consultation with organisations representing PWDs among others;
(c) promote design, production and distribution of accessible ICT at an early stage;
(d) ensure that persons with disabilities can exercise the right to access to information, freedom of expression and opinion;
(e) require both public and private entities that render services to the public to provide information and services in accessible and usable formats for persons with disabilities;
(f) Require content producers for distribution and public consumption in Kenya to produce such content in accessible format such as audio description, audio subtitles, captions and signing for access to persons with disabilities.
(g) ensure that websites of government departments and agencies comply with international web accessibility standards and are accessible for persons with disabilities
(h) provide incentives to providers of accessible technology solutions including software, hardware and applications
(i) take such measures that will lessen the burden of acquisition of accessible technologies and associated gadgets by PWDs through fiscal means such as tax exemptions, subsidization, funding acquisitions, etc.
(j) ensuring that licensed ICT service providers offer special tariff plans or discounted rates for persons with disabilities communicate with the rest of society.
(k) Ensure that licensed providers of telecommunications services make available services and supporting technologies for persons with disabilities including emergency services, accessible public phones and relay services to enable persons with speech, hearing and seeing disabilities
Similar sentiments were shared by lawyer and digital rights activist Angela Minayo, who said the workshop “was very productive” and had enabled participants to realise that there is a gap in the implementation of ICT policy and in awareness of how national policies and international legal frameworks provide for persons with disabilities to be able to access and use ICT.
Conversations from the workshop were carried forward to the KIGF, with a session on inclusion, where Okite joined Paul Kiage (Communications Authority), Nivi Sharma (BRCK), Ben Roberts (Liquid Telecom), Josephine Miliza (KICTANet) and Alfred Mugambi (Safaricom) on a panel.
Kiage, an assistant director in charge of the Universal Service Fund (USF), said the fund had collected KShs 9 billion (USD 86.6 million), mostly used to extend network coverage to areas without voice services and to offer broadband connection to 896 secondary schools across the 47 counties. He said they had installed JAWS software and other assistive devices in eight learning institutions, partnered with the National Council for Persons with Disabilities to create a portal to enable persons with disabilities to access information including job advertisements, and created platforms in some libraries to enable accessibility to digital content.
But, according to Okite, despite USF’s efforts, “the digital divide is growing bigger for persons with disabilities”. Research she was part of last year showed that computers in some of the learning institutions had not been replaced for several years, requisite software was not installed or out of date, and staff managing the labs were not trained to teach users. Sustainability of the initiative was thus in question.
Kiage’s response? “We could do a lot more because we know there’s even primary schools that are catering for persons with disabilities in Kenya so we could go lower and support such schools.”
As of March 2019, Kenya had a mobile penetration of 106%, or 51 million subscriptions, while internet subscriptions stood at 46.8 million, of which 46.7% were on broadband. But as the KIGF panel on inclusion heard, segments of Kenyans can not afford to use ICT, and those in rural areas, poor and uneducated women, and many persons with disabilities were cited.
Dr. Wairagala Wakabi of CIPESA asked the Kenya government to conduct a gap analysis to establish the unmet ICT needs of persons with disabilities, collect on a regular basis disaggregated data that shows how persons with different types of disabilities are using technology and the challenges hindering greater use, and invest a larger portion of universal service funds in promoting digital accessibility. He added that Kenya should grow awareness about assistive technologies and make these technologies affordable.
“We should leave no one behind when it comes to digital inclusion,” he said. “Clearly, the Communications Authority can do more to improve access for people with disabilities, including through the use of the Universal Service Fund,” he said.
The private sector needs to be compliant too, and to be held to account to fulfil its obligations. In Kenya, and indeed across Africa, Safaricom has been a pace-setter. Last November, it launched the DOT Braille Watch service to enable the use of its M-Pesa mobile money service by persons with disabilities, said Karimi Ruria, Public Policy Manager at the provider. In December 2017, Safaricom introduced the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) that enables visually impaired and blind customers to control their M-Pesa transactions.