Par Simone Toussi |
Les pays de la région sahélienne, tels que le Burkina Faso, le Mali et le Niger, présentent un environnement périlleux pour les défenseurs des droits humains, au moment où des régimes militaires s’enlisent au pouvoir. L’espace numérique, autrefois perçu comme un symbole de liberté d’expression et d’accès à une information plurielle, est progressivement assiégé, les droits à la vie privée, à la liberté d’expression et à l’accès et au partage d’informations y étant de plus en plus restreints.
Si ces pays font face à des problématiques numériques communes à d’autres pays francophones d’Afrique – interruptions d’Internet, surveillance étatique, censure en ligne et instrumentalisation des lois sur la cybersécurité et la désinformation –, le renversement des gouvernements civils par l’armée y a aggravé le niveau d’autoritarisme.
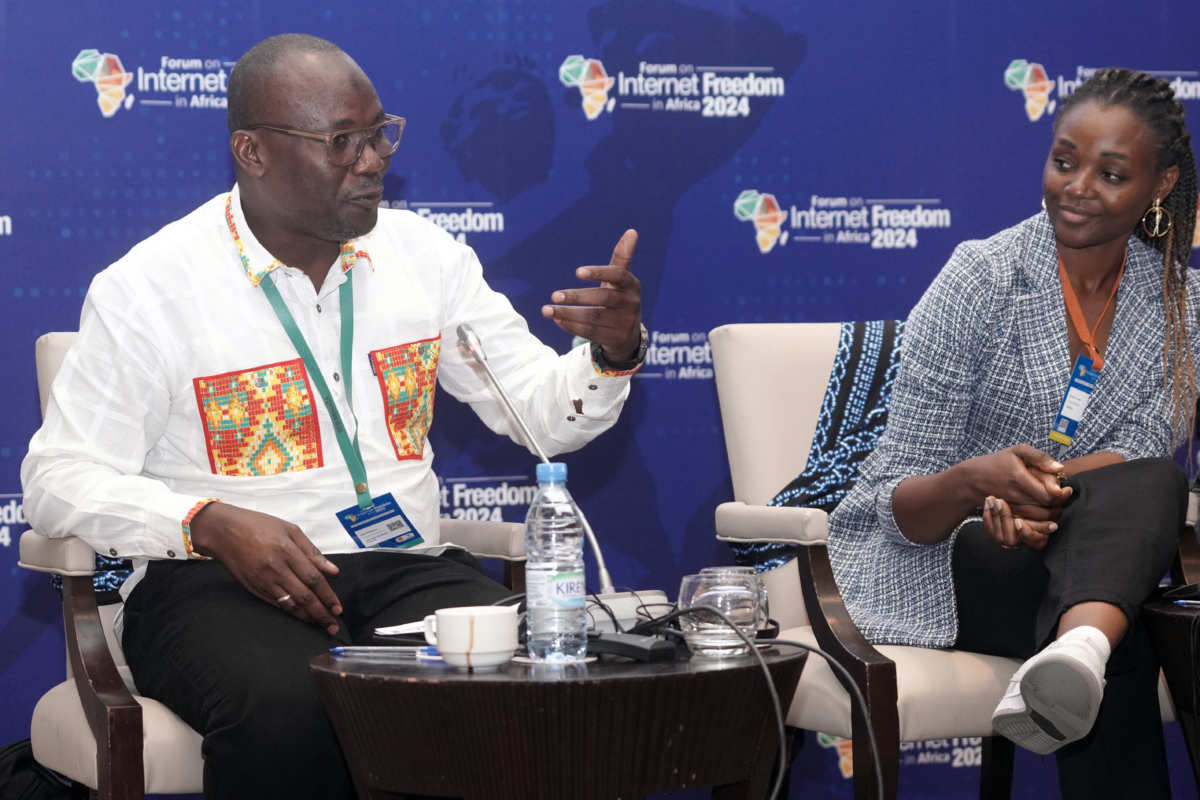
Lors du Forum sur la liberté de l’Internet en Afrique – organisé par la Collaboration sur les Politiques Internationales des TIC pour l’Afrique de l’Est et Australe (CIPESA) et AfricTivistes en septembre 2024 à Dakar, Sénégal – des experts se sont réunis pour discuter des défis croissants et des opportunités en matière de droits numériques dans la région. Le panel a élucidé la position précaire des défenseurs des droits humains et le rôle ambivalent des technologies numériques, qui exacerbent autant qu’elles offrent des solutions à ces défis.
Dans le cadre des efforts de CIPESA pour lutter contre les troubles de l’information en Afrique subsaharienne et équiper les acteurs au plaidoyer pour de lois numériques plus justes, le panel a abordé des questions critiques relatives aux droits numériques ainsi que des problématiques sociales pressantes comme l’inégalité de genre, les conflits armés et la détérioration de la liberté de la presse, tout en examinant le cadre réglementaire émergent y afférent.
Les défenseurs des droits humains au Sahel, notamment les activistes pour les droits des femmes et les journalistes, rencontrent d’immenses difficultés en raison de l’instabilité politique, de la violence armée et des régimes autoritaires, qui imposent de sévères restrictions à la liberté de la presse, à la circulation de l’information et aux activités de la société civile.
Djibril Saidou, de International Media Support (IMS), a souligné que les défis des droits numériques au Sahel vont au-delà de la protection de la liberté d’expression. « Il s’agit de garantir l’accès à l’information sur des questions urgentes comme les droits des femmes et les conflits armés », a-t-il déclaré. Dans ces contextes difficiles, il a affirmé que les efforts d’intervention devraient se concentrer sur la résistance à la censure et le renforcement de la résilience des défenseurs des droits numériques et de la démocratie.
Chantal Nare, blogueuse féministe de Bloggueuses226 et activiste burkinabè, a partagé son expérience de militante pour les droits des femmes dans un environnement aussi fragile. Elle a évoqué la peur constante de représailles et de surveillance, qui entrave l’expression libre, même sur les plateformes numériques. Chantal a soulevé une question cruciale : « Comment les plateformes numériques comme WhatsApp ou les blogs peuvent-elles être utilisées pour protéger et autonomiser les femmes sans les exposer à davantage de risques face aux acteurs étatiques ou extrémistes ? »
Urbain Yameogo, du Centre d’Information et de Formation sur les Droits Humains en Afrique (CIFDHA), a cité l’abus des lois sur la cybercriminalité et le terrorisme pour restreindre la liberté d’expression. « La loi antiterroriste de 2015 au Burkina Faso permettait aux journalistes un certain accès à des informations sensibles liées au terrorisme. Cependant, les révisions du Code pénal en 2019 ont supprimé ces exemptions, exposant les journalistes à des poursuites pour des actes qu’ils exerçaient dans le cadre de leur travail, comme l’accès aux sites liés au terrorisme. Cette modification a créé une zone grise juridique qui rend les journalistes et les défenseurs des droits humains vulnérables à des persécutions. »
Les panélistes ont souligné que les journalistes de la région, rapportant sur des sujets sensibles comme le terrorisme et les violations des droits humains, sont de plus en plus poursuivis sous des lois sur la cybercriminalité, plutôt que sous les lois traditionnelles sur la presse, qui offraient historiquement plus de protection. Ce changement compromet les droits des journalistes à rapporter librement, car les lois sur la cybercriminalité, souvent mal définies, peuvent être interprétées de manière extensive pour réprimer un travail journalistique légitime.
Face au défi de défendre les droits numériques dans un climat de peur des représailles des régimes militaires, certains participants ont souligné la nécessité d’exercer une prudence extrême et d’adopter une approche conciliatrice dans leur travail. Cheikh Fall, de l’organisation régionale des droits humains AfricTivistes, a affirmé : « Parfois, il faut choisir entre la vie et la liberté. Dans les pays du Sahel sous régime militaire, les droits numériques sont éclipsés par le besoin immédiat de survie. Cette réalité souligne que la lutte pour les droits humains fondamentaux est indissociable du combat pour la liberté. »
Des propositions ont été faites pour créer des lois unifiées traitant à la fois des enjeux numériques et médiatiques. Cependant, étant donné les craintes que ces lois puissent renforcer la répression plutôt que protéger les libertés, un dialogue inclusif et des processus politiques participatifs ont été jugés cruciaux. Cela permettrait de garantir une meilleure protection non seulement pour les journalistes et les défenseurs, mais aussi pour les femmes et d’autres groupes vulnérables. À cet égard, Chantal Nare a appelé à une législation englobant les formes de répression physique et numérique.
Outre les réformes juridiques, les panélistes ont également insisté sur la nécessité d’une formation renforcée à la sécurité numérique et d’une collaboration accrue entre les acteurs locaux et internationaux.