By CIPESA Writer |
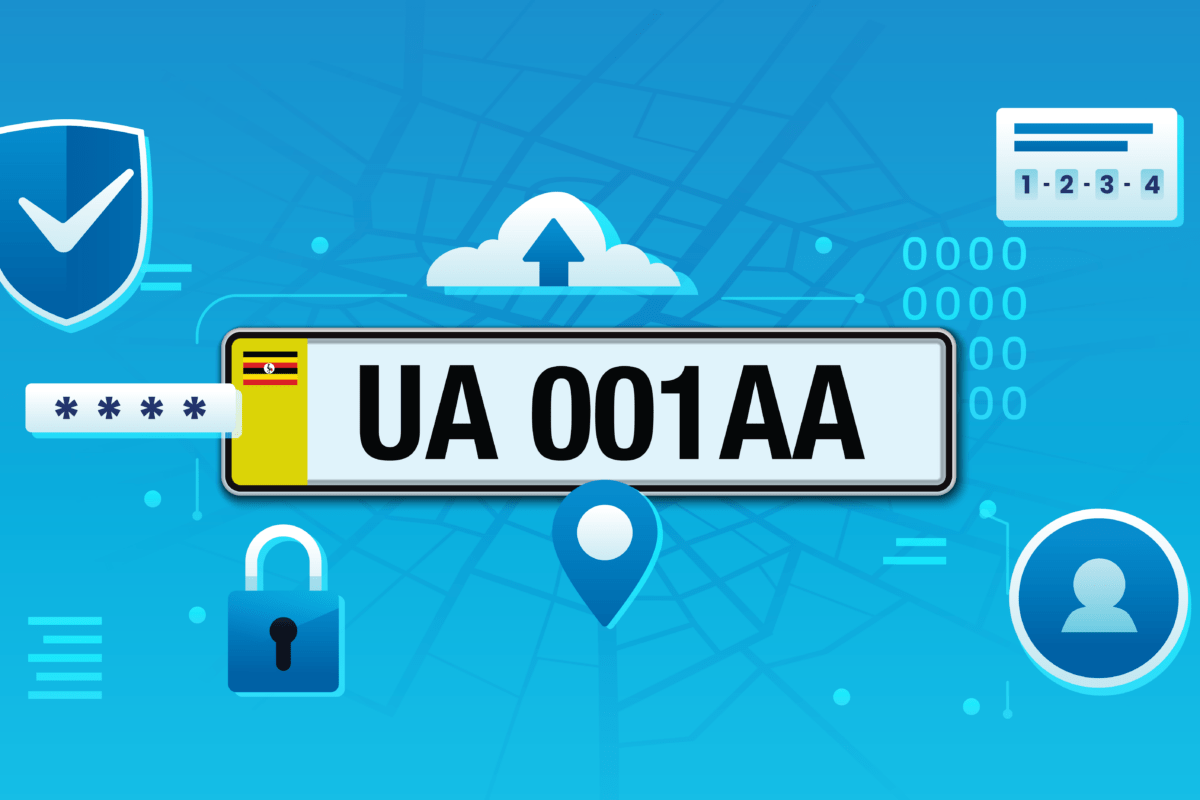
The rollout of the digital number plate system in Uganda is well underway. At a press conference last month, the Ministry of Works and Transport announced January 2025 as the deadline for full roll out. The system – over two years in the making – is a joint project between the government of Uganda and Russian company Joint Stock Company Global Security and has caused alarm among rights activists as it introduces another layer of massive personal data collection and processing amidst weak controls.
The stated objective of the Intelligent Transport Monitoring System (ITMS) is to improve the country’s transport management systems and security by enabling the authorities to “swiftly identify vehicles involved in criminal activities and improve traffic management through efficient ticketing and revenue collection”. It will involve the installation of digital number plates on all vehicles and motorcycles in the country, allowing security agencies to track and pinpoint their location at any one time.
| Overview of ITMS | ||
| Digital Number Plate Components | Status of Fitment on Government Vehicles as at June 2024 | Target Installations (Registered Vehicles as at July 2024) |
| Aluminium plates – front and back | 1,091 | 2,145, 988 |
| A tracker | ||
| A sim chip | ||
| Bluetooth beacons – front and back | ||
| Snap locks | ||
Once rolled out, the digital plates will add to the catalogue of surveillance apparatus in Uganda. The country already has a plethora of retrogressive laws, such as the Regulation of Interception of Communications Act 2010 and the Anti-Terrorism Act 2002 that require communication service providers to aid in intercepting communication by ensuring that their systems are always technically capable of supporting lawful interception. The laws also grant powers to an authorised officer to intercept the communications of a person and to conduct surveillance of individuals.
The components of the digital number plates will enable the government through its security agencies, such as the police, to swiftly identify vehicles and their owners. Instantaneous data exchanges pose major challenges to data privacy, especially in cases where there are calculated targets such as civil society organisations (CSOs), human rights defenders (HRDs), activists, and political opponents, government critics, or dissidents.
An added concern is that, according to the Uganda Police, the digital number plate system will be integrated with the Closed Circuit Television System (CCTV) system and others such as the motor vehicle registration system, the e-tax system managed by the Uganda Revenue Authority (URA) and the national identity database managed by the National Identification and Registration Authority (NIRA) to “ensure comprehensive vehicle and personal identification.” Given weak controls over data held by public bodies and rare punishment for data breaches and unauthorised access, linking these databases absent clear data-sharing frameworks and robust controls poses grave concerns. Notably, Uganda does not have a law or regulations governing CCTV/ video surveillance.
Whereas there are efforts to localise parts of the system through the establishment of a local production facility for the various components, the partnership with Joint Stock Company Global Security underscores Uganda’s reliance on foreign entities for purposes of conducting surveillance and interception of private communication of its citizens. For example, in August 2022, there were reports that the Uganda Police had purchased UFED, a technology developed by the Israeli firm Cellebrite that enables authorities to hack into password-protected smartphones.
Earlier, starting in 2018, Uganda turned to a Chinese company, Huawei, for the supply and installation of CCTV across major cities. The decision to install the CCTV cameras came on the heels of a spate of murders that had engulfed the country, with the security forces keen on using the CCTV cameras to improve security in the country. Like many other government security procurements, the CCTV deal raised a lot of transparency and accountability issues, including the secrecy that surrounded the entire process.
Additionally, there were reports that security agencies were working with Huawei technicians in Uganda to spy on opposition critics by intercepting encrypted communications and using cell data to track their movements. This appeared to be the continuation of a trend that was documented earlier in 2012, when the Uganda government reportedly relied on a Germany-made spyware, FinFisher, which it is said to have covertly installed in various places, including hotels, the parliament and key government institutions, for purposes of surveilling on its opponents, including politicians, civil society, and the media.
Given the country’s history of repressing the civic space and harassing political opponents, CSOs and HRDs, the ITMS digital number plates could further the suppression of civil liberties, including political participation, freedom of expression, access to information and assembly and association. Moreover, deeper democratic regression could occur since these liberties largely depend on privacy and the ability to express oneself with minimal interruptions or interference.
While the government has a legitimate desire to improve the security of its people and transport management, recent events as discussed above where the same government has used the acquired technologies to surveil its citizens and undermine digital rights, it is critical that any future attempt to enhance its surveillance apparatus is anchored in law with clear oversight mechanisms. This is because the deployment of surveillance technologies such as ITMS, FinFisher, and Huawei’s CCTV present a veritable avenue for economic and political exploitation by collecting extensive data on people’s behaviour, location, activities, and interests online and offline. This makes the risk of violation of privacy apparent, rendering citizens helpless because they essentially have no control over how the data will be used, even when they are aware that data is being collected.
It is, therefore, important that the government reduce its reliance on foreign-manufactured surveillance technologies, particularly from countries whose human rights record is wanting, as these have tended to use these tools to suppress civic spaces. In addition, the government should reconsider its regulatory framework to ensure it conforms to international standards on privacy and data protection, especially during the procurement and deployment of potentially intrusive technology that is prone to abuse.