By CIPESA Writer |
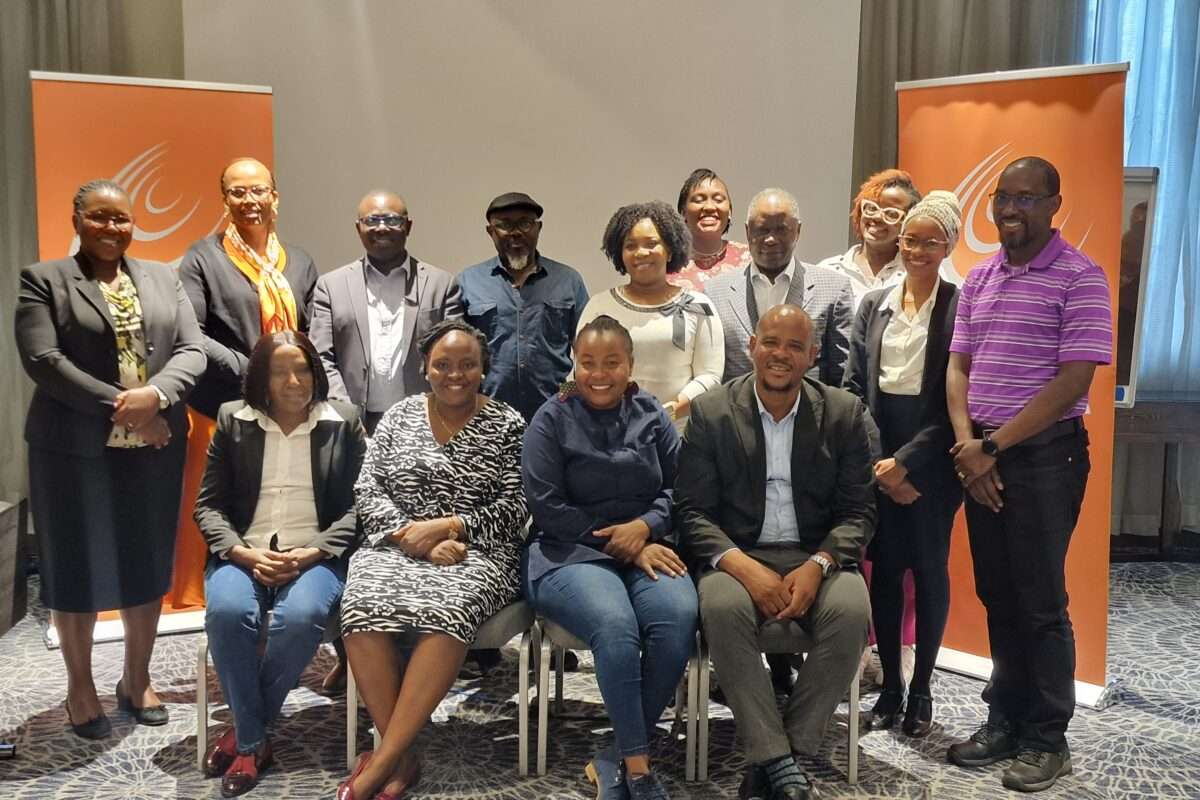
As part of its ongoing efforts to enhance the ability of African National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) to monitor, protect, and promote digital freedoms, the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) last month conducted a two-day capacity-building training that attracted NHRI representatives from Lesotho, Mozambique, Tanzania, Uganda, Zimbabwe, and Zambia.
The two-day training that was held in Nairobi, Kenya, on June 25 and 26, 2024, sought to empower staff of NHRIs in the region to engage with the opportunities and challenges that digital technology poses for human rights protection and monitoring of digital rights. In his opening remarks, CIPESA Executive Director Dr. Wairagala Wakabi noted that NHRIs play a critical role in the protection and promotion of human rights, and given the deteriorating state of digital rights in the region, it was important that they are equipped to deal with the intersection between the digital and the traditional human rights. According to the Paris Principles, NHRIs are required to have a broad mandate that allows them to effectively execute their mandate of promoting and protecting human rights, both offline and online.
The Nairobi training followed a similar training that CIPESA conducted in Ethiopia for staff of the Ethiopian Human Rights Commission (EHRC), who identified key actions the commission could integrate in its annual work plans, such as digital rights monitoring, advocacy for enabling laws to be enacted, and developing tools for follow up on implementation of recommendations on digital rights by treaty bodies and the United Nations Human Rights Council.
Digital Rights as Human Rights
Digital rights have been recognised at both international and regional levels. For example, in 2018, during its 38th session, the United Nations Human Rights Council adopted resolution A/HRC/RES/38/7 that reaffirmed that “the same rights that people have offline must also be protected online.” In 2016, the United Nations General Assembly passed a non-binding resolution on “the promotion, protection, and enjoyment of human rights on the Internet,” condemning any measures taken by state parties to prevent or disrupt internet access and calling upon them to refrain from and cease any such measures.
In March 2024, the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights passed resolution ACHPR.Res.580 (LXXVIII)2024 on Internet Shutdowns and Elections in Africa “reaffirming the importance of access to the internet in the digital age and its implication for the realisation of human rights”. The resolution called upon member states to “refrain from ordering the interruption of telecommunications services, shutting down the internet, and/or disrupting access to any other digital communication platforms before, during or after the elections.”
Challenges Facing NHRIs
In many cases, African NHRIs have found themselves operating in an increasingly hostile environment with limited funding and hostility from state agencies, who sometimes view their role as countering and incriminating the government in human rights violations. In addition, because of the limited funding, many NHRIs are not in a position to recruit or improve the level of expertise among their staff members, especially when it comes to new and emerging technologies and how they affect the enjoyment of human rights. Participants acknowledged that, in many cases, they are always playing catch-up when it comes to legislation, yet they are supposed to be the primary advisors and reviewers of draft laws related to human rights.
In his remarks, Victor Kapiyo, one of the trainers, noted that the adoption of digital technologies has brought up new human rights issues, particularly as governments have reacted by enacting laws that have, for the most part, served to stifle human rights as opposed to facilitating their enjoyment. On the other hand, digital technologies have also facilitated the spread of hate speech, disinformation, and technology-facilitated gender-based violence. It is important that NHRIs keep enhancing their capacity to monitor, investigate, and protect against violations of digital rights by both governments and private actors, including big tech companies.
Practical Strategies for NHRIs
During the training, participants discussed an array of strategies that they can adopt to monitor, document, and protect digital rights, including the use of practical legal and policy guidance set out in the Rabat Plan of Action, as well as Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights when engaging with governments and business entities especially technological companies in regards to their obligations to respect, protect and promote human rights.
Participants also noted the need to engage with security agencies, the justice department, and policymakers on issues of digital rights. It was noted that because the concept of digital rights in Africa is new and evolving with limited understanding and jurisprudence, NHRIs need to constantly retool themselves on the emerging issues if they are to execute their mandates effectively. Other strategies included building coalitions and collaborations with civil society actors, the media and academia to help unpack and create awareness about digital rights.
The training was facilitated by trainers from CIPESA, Internews, the International Centre for Non-Profit Law, and the Kenya National Cohesion and Integration Commission (NCIC).