By Juliet Nanfuka |
In 2015, the 38th General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) endorsed a new definition on the universality of the internet. It was based upon four principles, namely Rights, Openness, Accessibility to all and Multi-stakeholder participation, or the ROAM principles.
The addition of cross-cutting indicators in 2018 resulted in the ROAM-X Indicator framework comprising 303 indicators that assess the extent to which national stakeholders, including governments, businesses and civil society, comply with the ROAM principles. It was recognised that these indicators were central to the growth and evolution of the internet, and the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
Over the years, UNESCO has partnered with the Collaboration on International ICT Policy for East and Southern Africa (CIPESA) to increase awareness of the Internet Universality Indicators (IUI’s) and the ROAM-X framework. In 2015, at the CIPESA-convened Forum on Internet Freedom in Africa (FIFAfrica), the ROAM principles were featured in the opening discussion of the event, with then UNESCO regional advisor for Communication and Information, Jaco du Toit, explaining the practical use of the Internet Universality principles of human-rights, openness, accessibility and multi-stakeholder participation and their link to African development.
The 2018 edition of FIFAfrica again provided a collaborative platform for experts, policymakers, activists, and technologists to exchange ideas and strategies for advancing a more inclusive and accessible digital space. CIPESA also contributed to discussions at the 2018 Internet Governance Forum (IGF) where the link between internet shutdowns and the need for national assessments through the use of the ROAM-X framework was stressed.
At the October 2020 Africa IGF, CIPESA contributed to a discussion that served as a launch of the IGF Dynamic Coalition on Internet Universality Indicators (IUIs). The Dynamic Coalition is a shared space for advocating Internet Universality ROAM principles worldwide, sharing experiences and raising awareness of the value of the related indicators and good practice in applying them in more countries. Further discussions were held at the global IGF in November 2020.
In March 2022, CIPESA hosted a regional dialogue on the Indicators, which highlighted lessons from countries where IUI assessments had been conducted, namely Benin, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Niger and Senegal. This effort aimed to garner best practices in conducting national assessments of media and internet ecosystems using the indicators.
Later that year, CIPESA convened a regional training webinar to raise awareness of the Internet Universality ROAM-X indicators and their potential to promote internet development to advance media freedom and digital rights in Africa. The UNESCO Information for All Programme (IFAP) and International Programme for the Development of Communication (IPDC) jointly supported the training which targeted participants from Cameroon, Malawi, Namibia, Somalia and Uganda. Outputs from the webinar went on to feed into discussions at the 2022 IGF which included sessions on the ROAM-X indicators and a session on the Internet Universality Indicators as part of the Dynamic Coalition.
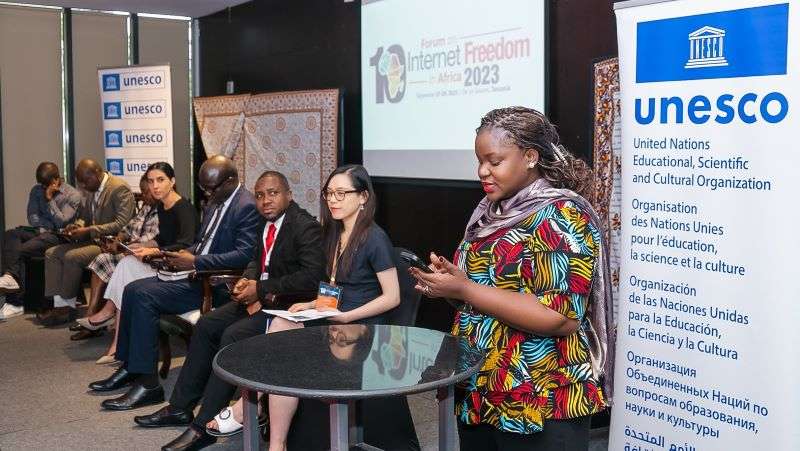
At the 2023 edition of FIFAfrica held in September in Tanzania, UNESCO hosted a session titled “Foster Internet Freedom in Africa through UNESCO’s ROAM-X Internet Universality Indicators Assessments”. The panel consisted of UNESCO experts, including John Okande, Programme Officer, Tatevik Grigoryan, Associate Programme Specialist; and Xiaojie Sun, Junior Professional Officer. Also on the panel were participants from earlier UNESCO/CIPESA collaborative efforts on ROAM-X, including Asrat M. Beyene from the Internet Society Ethiopia Chapter and Addis Ababa Science and Technology University; Grace Githaiga, Convenor of the Kenya ICT Action Network (KICTANet); and Dr. Simon-Peter Kafui Aheto of the University of Ghana.
The various speakers showcased the main findings and recommendations from the IUI assessments they conducted, and impacts of ongoing and completed ROAM-X national assessments in Africa (see some assessments here). They also shared best practices and lessons learnt during the implementation process. Panelists also highlighted that the IUI is due for revision following the amount of data collected over the years and the evolving digital landscape globally. Since its introduction, ROAM-X has been integrated into discussions at FIFAfrica and into CIPESA programming, both of which have served as collaborative platforms for experts and policymakers to advance inclusivity and accessibility in the digital space.